Page 38 - The Handbook for Quality Management a Complete Guide to Operational Excellence
P. 38
24 B u s i n e s s - I n t e g r a t e d Q u a l i t y S y s t e m s T h e Q u a l i t y F u n c t i o n 25
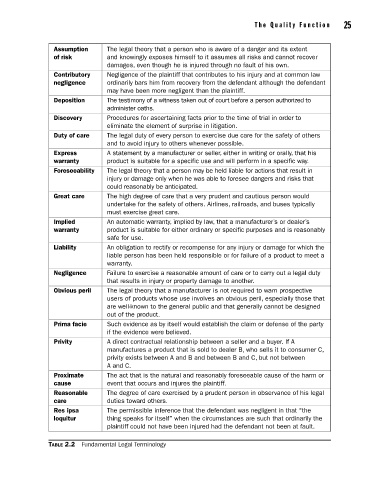
Assumption The legal theory that a person who is aware of a danger and its extent
of risk and knowingly exposes himself to it assumes all risks and cannot recover
damages, even though he is injured through no fault of his own.
Contributory Negligence of the plaintiff that contributes to his injury and at common law
negligence ordinarily bars him from recovery from the defendant although the defendant
may have been more negligent than the plaintiff.
Deposition The testimony of a witness taken out of court before a person authorized to
administer oaths.
Discovery Procedures for ascertaining facts prior to the time of trial in order to
eliminate the element of surprise in litigation.
Duty of care The legal duty of every person to exercise due care for the safety of others
and to avoid injury to others whenever possible.
Express A statement by a manufacturer or seller, either in writing or orally, that his
warranty product is suitable for a specific use and will perform in a specific way.
Foreseeability The legal theory that a person may be held liable for actions that result in
injury or damage only when he was able to foresee dangers and risks that
could reasonably be anticipated.
Great care The high degree of care that a very prudent and cautious person would
undertake for the safety of others. Airlines, railroads, and buses typically
must exercise great care.
Implied An automatic warranty, implied by law, that a manufacturer’s or dealer’s
warranty product is suitable for either ordinary or specific purposes and is reason ably
safe for use.
Liability An obligation to rectify or recompense for any injury or damage for which the
liable person has been held responsible or for failure of a product to meet a
warranty.
Negligence Failure to exercise a reasonable amount of care or to carry out a legal duty
that results in injury or property damage to another.
Obvious peril The legal theory that a manufacturer is not required to warn prospec tive
users of products whose use involves an obvious peril, especially those that
are well-known to the general public and that generally cannot be designed
out of the product.
Prima facie Such evidence as by itself would establish the claim or defense of the party
if the evidence were believed.
Privity A direct contractual relationship between a seller and a buyer. If A
manufactures a product that is sold to dealer B, who sells it to consumer C,
privity exists between A and B and between B and C, but not between
A and C.
Proximate The act that is the natural and reasonably foreseeable cause of the harm or
cause event that occurs and injures the plaintiff.
Reasonable The degree of care exercised by a prudent person in observance of his legal
care duties toward others.
Res ipsa The permissible inference that the defendant was negligent in that “the
loquitur thing speaks for itself” when the circumstances are such that ordinarily the
plaintiff could not have been injured had the defendant not been at fault.
Table 2.2 Fundamental Legal Terminology
02_Pyzdek_Ch02_p015-030.indd 25 11/16/12 4:46 PM