Page 19 - The Illustrated Dictionary of Electronics
P. 19
5059F-pA_1-55 4/9/01 4:41 PM Page 4
4 absolute units • A-B test
absolute units Fundamental physical units (see into heat or other forms of energy. 2. Loss of all or
ABSOLUTE SYSTEM OF UNITS) from which all part of a skywave because of absorption by the
others are derived. See, for example, AMPERE, ionosphere. Also called ionospheric absorption or
OHM, VOLT, and WATT. atmospheric absorption.
absolute value The magnitude of a quantity with- absorption marker A small blip introduced onto
out regard to sign or direction. The absolute value an oscilloscope trace to indicate a frequency
of a is written |a|. The absolute value of a posi- point. It is so called because it is produced by the
tive number is the number itself; thus, |10| action of a frequency-calibrated tuned trap, simi-
equals 10. The absolute value of a negative num- lar to an absorption wavemeter.
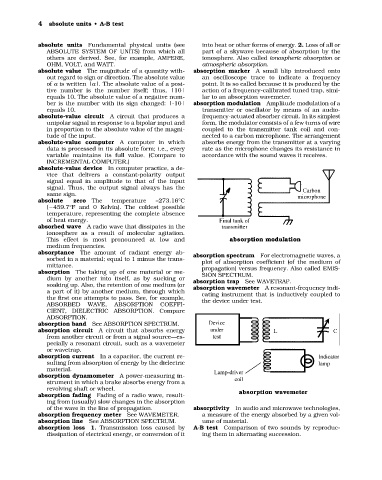
ber is the number with its sign changed: |-10| absorption modulation Amplitude modulation of a
equals 10. transmitter or oscillator by means of an audio-
absolute-value circuit A circuit that produces a frequency-actuated absorber circuit. In its simplest
unipolar signal in response to a bipolar input and form, the modulator consists of a few turns of wire
in proportion to the absolute value of the magni- coupled to the transmitter tank coil and con-
tude of the input. nected to a carbon microphone. The arrangement
absolute-value computer A computer in which absorbs energy from the transmitter at a varying
data is processed in its absolute form; i.e., every rate as the microphone changes its resistance in
variable maintains its full value. (Compare to accordance with the sound waves it receives.
INCREMENTAL COMPUTER.)
absolute-value device In computer practice, a de-
vice that delivers a constant-polarity output
signal equal in amplitude to that of the input
signal. Thus, the output signal always has the
same sign.
absolute zero The temperature –273.16°C
( 459.7°F and 0 Kelvin). The coldest possible
temperature, representing the complete absence
of heat energy.
absorbed wave A radio wave that dissipates in the
ionosphere as a result of molecular agitation.
This effect is most pronounced at low and
medium frequencies.
absorptance The amount of radiant energy ab- absorption spectrum For electromagnetic waves, a
sorbed in a material; equal to 1 minus the trans- plot of absorption coefficient (of the medium of
mittance. propagation) versus frequency. Also called EMIS-
absorption The taking up of one material or me- SION SPECTRUM.
dium by another into itself, as by sucking or absorption trap See WAVETRAP.
soaking up. Also, the retention of one medium (or absorption wavemeter A resonant-frequency indi-
a part of it) by another medium, through which cating instrument that is inductively coupled to
the first one attempts to pass. See, for example, the device under test.
ABSORBED WAVE, ABSORPTION COEFFI-
CIENT, DIELECTRIC ABSORPTION. Compare
ADSORPTION.
absorption band See ABSORPTION SPECTRUM.
absorption circuit A circuit that absorbs energy
from another circuit or from a signal source—es-
pecially a resonant circuit, such as a wavemeter
or wavetrap.
absorption current In a capacitor, the current re-
sulting from absorption of energy by the dielectric
material.
absorption dynamometer A power-measuring in-
strument in which a brake absorbs energy from a
revolving shaft or wheel.
absorption fading Fading of a radio wave, result-
ing from (usually) slow changes in the absorption
of the wave in the line of propagation. absorptivity In audio and microwave technologies,
absorption frequency meter See WAVEMETER. a measure of the energy absorbed by a given vol-
absorption line See ABSORPTION SPECTRUM. ume of material.
absorption loss 1. Transmission loss caused by A-B test Comparison of two sounds by reproduc-
dissipation of electrical energy, or conversion of it ing them in alternating succession.