Page 23 - The Illustrated Dictionary of Electronics
P. 23
5059F-pA_1-55 4/9/01 4:41 PM Page 8
8 ac meter • acoustic feedback
ac meter A meter that is intended to work only on quencies. If one fork is struck and then brought
alternating current or voltage. Such meters in- near the other, the second fork will begin vibrating.
clude iron-vane and rectifier types. If the second fork has a fundamental frequency
that is a harmonic of the frequency of the first fork,
the second fork will vibrate at its own resonant
frequency. See HARMONIC, RESONANCE.
acoustic coupling Data transfer via a sound link
between a telephone and a pickup/reproducer.
Was once common in computer terminals and
facsimile machines. This scheme has been largely
replaced by hard wiring and optical coupling.
acoustic damping The deadening or reduction of
the vibration of a body to eliminate (or cause to
die out quickly) sound waves arising from it.
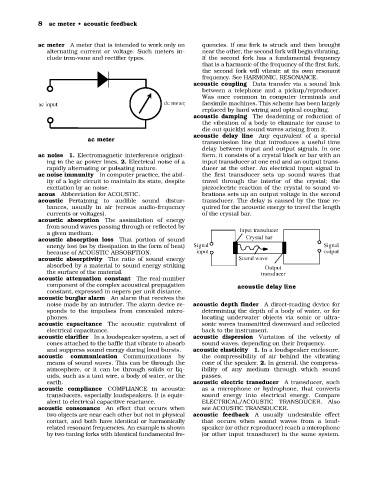
acoustic delay line Any equivalent of a special
transmission line that introduces a useful time
delay between input and output signals. In one
ac noise 1. Electromagnetic interference originat- form, it consists of a crystal block or bar with an
ing in the ac power lines. 2. Electrical noise of a input transducer at one end and an output trans-
rapidly alternating or pulsating nature. ducer at the other. An electrical input signal in
ac noise immunity In computer practice, the abil- the first transducer sets up sound waves that
ity of a logic circuit to maintain its state, despite travel through the interior of the crystal; the
excitation by ac noise. piezoelectric reaction of the crystal to sound vi-
acous Abbreviation for ACOUSTIC. brations sets up an output voltage in the second
acoustic Pertaining to audible sound distur- transducer. The delay is caused by the time re-
bances, usually in air (versus audio-frequency quired for the acoustic energy to travel the length
currents or voltages). of the crystal bar.
acoustic absorption The assimilation of energy
from sound waves passing through or reflected by
a given medium.
acoustic absorption loss That portion of sound
energy lost (as by dissipation in the form of heat)
because of ACOUSTIC ABSORPTION.
acoustic absorptivity The ratio of sound energy
absorbed by a material to sound energy striking
the surface of the material.
acoustic attenuation constant The real-number
component of the complex acoustical propagation
constant, expressed in nepers per unit distance.
acoustic burglar alarm An alarm that receives the
noise made by an intruder. The alarm device re- acoustic depth finder A direct-reading device for
sponds to the impulses from concealed micro- determining the depth of a body of water, or for
phones. locating underwater objects via sonic or ultra-
acoustic capacitance The acoustic equivalent of sonic waves transmitted downward and reflected
electrical capacitance. back to the instrument.
acoustic clarifier In a loudspeaker system, a set of acoustic dispersion Variation of the velocity of
cones attached to the baffle that vibrate to absorb sound waves, depending on their frequency.
and suppress sound energy during loud bursts. acoustic elasticity 1. In a loudspeaker enclosure,
acoustic communication Communications by the compressibility of air behind the vibrating
means of sound waves. This can be through the cone of the speaker. 2. In general, the compress-
atmosphere, or it can be through solids or liq- ibility of any medium through which sound
uids, such as a taut wire, a body of water, or the passes.
earth. acoustic electric transducer A transducer, such
acoustic compliance COMPLIANCE in acoustic as a microphone or hydrophone, that converts
transducers, especially loudspeakers. It is equiv- sound energy into electrical energy. Compare
alent to electrical capacitive reactance. ELECTRICAL/ACOUSTIC TRANSDUCER. Also
acoustic consonance An effect that occurs when see ACOUSTIC TRANSDUCER.
two objects are near each other but not in physical acoustic feedback A usually undesirable effect
contact, and both have identical or harmonically that occurs when sound waves from a loud-
related resonant frequencies. An example is shown speaker (or other reproducer) reach a microphone
by two tuning forks with identical fundamental fre- (or other input transducer) in the same system.