Page 33 - The Illustrated Dictionary of Electronics
P. 33
5059F-pA_1-55 4/9/01 4:41 PM Page 18
18 aircraft flutter • airwaves
aircraft flutter Rapid, repetitive fading and inten-
sifying of a received radio or television signal, re-
sulting from reflections of the signal by passing
aircraft.
aircraft station A nonautomatic radio communi-
cations station installed on an aircraft.
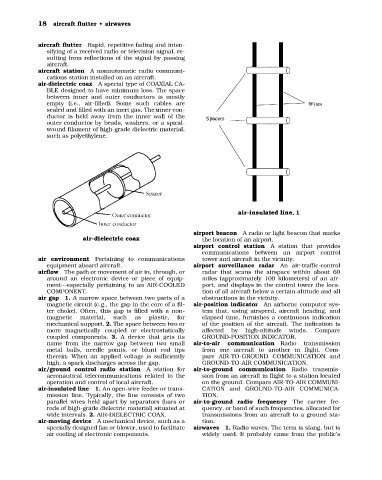
air-dielectric coax A special type of COAXIAL CA-
BLE designed to have minimum loss. The space
between inner and outer conductors is mostly
empty (i.e., air-filled). Some such cables are
sealed and filled with an inert gas. The inner con-
ductor is held away from the inner wall of the
outer conductor by beads, washers, or a spiral-
wound filament of high-grade dielectric material,
such as polyethylene.
airport beacon A radio or light beacon that marks
the location of an airport.
airport control station A station that provides
communications between an airport control
air environment Pertaining to communications tower and aircraft in the vicinity.
equipment aboard aircraft. airport surveillance radar An air-traffic-control
airflow The path or movement of air in, through, or radar that scans the airspace within about 60
around an electronic device or piece of equip- miles (approximately 100 kilometers) of an air-
ment—especially pertaining to an AIR-COOLED port, and displays in the control tower the loca-
COMPONENT. tion of all aircraft below a certain altitude and all
air gap 1. A narrow space between two parts of a obstructions in the vicinity.
magnetic circuit (e.g., the gap in the core of a fil- air-position indicator An airborne computer sys-
ter choke). Often, this gap is filled with a non- tem that, using airspeed, aircraft heading, and
magnetic material, such as plastic, for elapsed time, furnishes a continuous indication
mechanical support. 2. The space between two or of the position of the aircraft. The indication is
more magnetically coupled or electrostatically affected by high-altitude winds. Compare
coupled components. 3. A device that gets its GROUND-POSITION INDICATOR.
name from the narrow gap between two small air-to-air communication Radio transmission
metal balls, needle points, or blunt rod tips from one aircraft to another in flight. Com-
therein. When an applied voltage is sufficiently pare AIR-TO-GROUND COMMUNICATION and
high, a spark discharges across the gap. GROUND-TO-AIR COMMUNICATION.
air/ground control radio station A station for air-to-ground communication Radio transmis-
aeronautical telecommunications related to the sion from an aircraft in flight to a station located
operation and control of local aircraft. on the ground. Compare AIR-TO-AIR COMMUNI-
air-insulated line 1. An open-wire feeder or trans- CATION and GROUND-TO-AIR COMMUNICA-
mission line. Typically, the line consists of two TION.
parallel wires held apart by separators (bars or air-to-ground radio frequency The carrier fre-
rods of high-grade dielectric material) situated at quency, or band of such frequencies, allocated for
wide intervals. 2. AIR-DIELECTRIC COAX. transmissions from an aircraft to a ground sta-
air-moving device A mechanical device, such as a tion.
specially designed fan or blower, used to facilitate airwaves 1. Radio waves. The term is slang, but is
air cooling of electronic components. widely used. It probably came from the public’s