Page 86 - The Illustrated Dictionary of Electronics
P. 86
5059F-pB_56-92 4/9/01 4:45 PM Page 71
biased search • bifilar electrometer 71
N N
P P
λ/4
Reverse Forward
bias bias
Feed
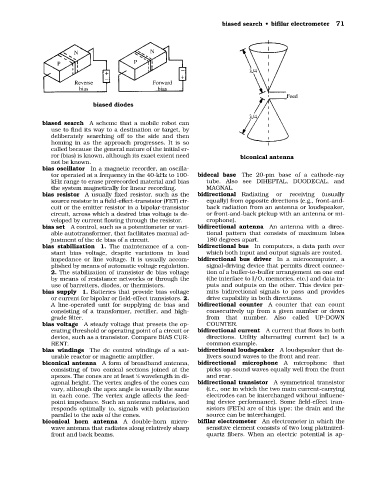
biased diodes
λ/4
biased search A scheme that a mobile robot can
use to find its way to a destination or target, by
deliberately searching off to the side and then
homing in as the approach progresses. It is so
called because the general nature of the initial er-
ror (bias) is known, although its exact extent need biconical antenna
not be known.
bias oscillator In a magnetic recorder, an oscilla-
tor operated at a frequency in the 40-kHz to 100- bidecal base The 20-pin base of a cathode-ray
kHz range to erase prerecorded material and bias tube. Also see DIHEPTAL, DUODECAL, and
the system magnetically for linear recording. MAGNAL.
bias resistor A usually fixed resistor, such as the bidirectional Radiating or receiving (usually
source resistor in a field-effect-transistor (FET) cir- equally) from opposite directions (e.g., front-and-
cuit or the emitter resistor in a bipolar-transistor back radiation from an antenna or loudspeaker,
circuit, across which a desired bias voltage is de- or front-and-back pickup with an antenna or mi-
veloped by current flowing through the resistor. crophone).
bias set A control, such as a potentiometer or vari- bidirectional antenna An antenna with a direc-
able autotransformer, that facilitates manual ad- tional pattern that consists of maximum lobes
justment of the dc bias of a circuit. 180 degrees apart.
bias stabilization 1. The maintenance of a con- bidirectional bus In computers, a data path over
stant bias voltage, despite variations in load which both input and output signals are routed.
impedance or line voltage. It is usually accom- bidirectional bus driver In a microcomputer, a
plished by means of automatic voltage regulation. signal-driving device that permits direct connec-
2. The stabilization of transistor dc bias voltage tion of a buffer-to-buffer arrangement on one end
by means of resistance networks or through the (the interface to I/O, memories, etc.) and data in-
use of barretters, diodes, or thermistors. puts and outputs on the other. This device per-
bias supply 1. Batteries that provide bias voltage mits bidirectional signals to pass and provides
or current for bipolar or field-effect transistors. 2. drive capability in both directions.
A line-operated unit for supplying dc bias and bidirectional counter A counter that can count
consisting of a transformer, rectifier, and high- consecutively up from a given number or down
grade filter. from that number. Also called UP-DOWN
bias voltage A steady voltage that presets the op- COUNTER.
erating threshold or operating point of a circuit or bidirectional current A current that flows in both
device, such as a transistor. Compare BIAS CUR- directions. Utility alternating current (ac) is a
RENT. common example.
bias windings The dc control windings of a sat- bidirectional loudspeaker A loudspeaker that de-
urable reactor or magnetic amplifier. livers sound waves to the front and rear.
biconical antenna A form of broadband antenna, bidirectional microphone A microphone that
consisting of two conical sections joined at the picks up sound waves equally well from the front
apexes. The cones are at least ⁄4 wavelength in di- and rear.
1
agonal height. The vertex angles of the cones can bidirectional transistor A symmetrical transistor
vary, although the apex angle is usually the same (i.e., one in which the two main current-carrying
in each cone. The vertex angle affects the feed- electrodes can be interchanged without influenc-
point impedance. Such an antenna radiates, and ing device performance). Some field-effect tran-
responds optimally to, signals with polarization sistors (FETs) are of this type; the drain and the
parallel to the axis of the cones. source can be interchanged.
biconical horn antenna A double-horn micro- bifilar electrometer An electrometer in which the
wave antenna that radiates along relatively sharp sensitive element consists of two long platinized-
front and back beams. quartz fibers. When an electric potential is ap-