Page 91 - The Illustrated Dictionary of Electronics
P. 91
5059F-pB_56-92 4/9/01 4:45 PM Page 76
76 bismuth • black box
bismuth Symbol, Bi. A metallic element. Atomic terrelated smaller capacity processors (e.g., a 16-
number, 83. Atomic weight, 209. bit unit derived from eight 2-bit “slices”).
bismuth flux meter A flux meter in which the sen- bits per second Abbreviation, bps. An expression
sor contains a length of bismuth wire, which acts of digital data speed. Commonly used in com-
as a magnetoresistor. puter communications. This unit is often con-
bismuth thermocouple A thermocouple that uses fused with, and improperly called, the baud.
the junction between bismuth and antimony There is generally a difference between the speed
wires. Used in thermocouple-type meters. of a signal in baud, and the speed of the same sig-
bistable Having two stable states. nal in bps. Compare BAUD.
bistable device Any device, such as a flip-flop, the bitter pattern A pattern produced in a suspension
operation of which exhibits two stable states and of ferromagnetic powder in the presence of an im-
which can be switched at will from one state to perfection in a magnet. The pattern appears as an
the other. irregularity that is easy to see.
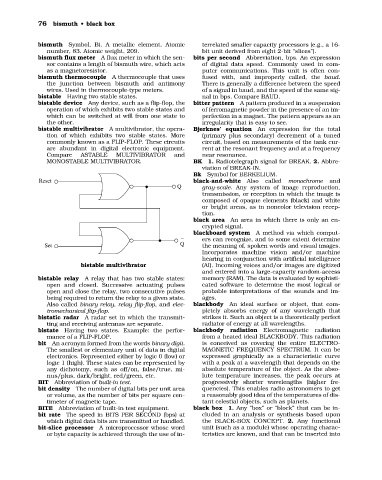
bistable multivibrator A multivibrator, the opera- Bjerknes’ equation An expression for the total
tion of which exhibits two stable states. More (primary plus secondary) decrement of a tuned
commonly known as a FLIP-FLOP. These circuits circuit, based on measurements of the tank cur-
are abundant in digital electronic equipment. rent at the resonant frequency and at a frequency
Compare ASTABLE MULTIVIBRATOR and near resonance.
MONOSTABLE MULTIVIBRATOR. BK 1. Radiotelegraph signal for BREAK. 2. Abbre-
viation of BREAK-IN.
Bk Symbol for BERKELIUM.
Reset black-and-white Also called monochrome and
Q gray-scale. Any system of image reproduction,
transmission, or reception in which the image is
composed of opaque elements (black) and white
or bright areas, as in noncolor television recep-
tion.
black area An area in which there is only an en-
crypted signal.
blackboard system A method via which comput-
− ers can recognize, and to some extent determine
Set Q the meaning of, spoken words and visual images.
Incorporates machine vision and/or machine
hearing in conjunction with artificial intelligence
bistable multivibrator (AI). Incoming voices and/or images are digitized
and entered into a large-capacity random-access
bistable relay A relay that has two stable states: memory (RAM). The data is evaluated by sophisti-
open and closed. Successive actuating pulses cated software to determine the most logical or
open and close the relay, two consecutive pulses probable interpretations of the sounds and im-
being required to return the relay to a given state. ages.
Also called binary relay, relay flip-flop, and elec- blackbody An ideal surface or object, that com-
tromechanical flip-flop. pletely absorbs energy of any wavelength that
bistatic radar A radar set in which the transmit- strikes it. Such an object is a theoretically perfect
ting and receiving antennas are separate. radiator of energy at all wavelengths.
bistate Having two states. Example: the perfor- blackbody radiation Electromagnetic radiation
mance of a FLIP-FLOP. from a heated ideal BLACKBODY. This radiation
bit An acronym formed from the words binary digit. is conceived as covering the entire ELECTRO-
The smallest or elementary unit of data in digital MAGNETIC FREQUENCY SPECTRUM. It can be
electronics. Represented either by logic 0 (low) or expressed graphically as a characteristic curve
logic 1 (high). These states can be represented by with a peak at a wavelength that depends on the
any dichotomy, such as off/on, false/true, mi- absolute temperature of the object. As the abso-
nus/plus, dark/bright, red/green, etc. lute temperature increases, the peak occurs at
BIT Abbreviation of built-in test. progressively shorter wavelengths (higher fre-
bit density The number of digital bits per unit area quencies). This enables radio astronomers to get
or volume, as the number of bits per square cen- a reasonably good idea of the temperatures of dis-
timeter of magnetic tape. tant celestial objects, such as planets.
BITE Abbreviation of built-in test equipment. black box 1. Any “box” or “block” that can be in-
bit rate The speed in BITS PER SECOND (bps) at cluded in an analysis or synthesis based upon
which digital data bits are transmitted or handled. the BLACK-BOX CONCEPT. 2. Any functional
bit-slice processor A microprocessor whose word unit (such as a module) whose operating charac-
or byte capacity is achieved through the use of in- teristics are known, and that can be inserted into