Page 93 - The Illustrated Dictionary of Electronics
P. 93
5059F-pB_56-92 4/9/01 4:45 PM Page 78
78 bleeder temperature • blocking interference
Bloch functions Solutions of the Schrodinger
+V 4
wave equation for a single electron surrounded
by an electric field. The field varies periodically
with distance from the source.
Bloch wall The transition layer between adjacent
ferromagnetic domains (see DOMAIN).
block 1. A group of data words or digits. 2. A group
+V 3
of memory storage spaces. 3. A circuit that oper-
ates as an identifiable unit. 4. The symbol for a
+ circuit, stage, unit, or device in a BLOCK DIA-
GRAM.
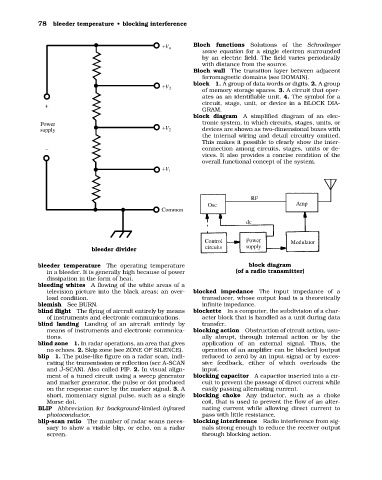
block diagram A simplified diagram of an elec-
Power tronic system, in which circuits, stages, units, or
supply +V 2 devices are shown as two-dimensional boxes with
the internal wiring and detail circuitry omitted.
This makes it possible to clearly show the inter-
− connection among circuits, stages, units or de-
vices. It also provides a concise rendition of the
overall functional concept of the system.
+V 1
RF
Osc Amp
Common
dc
Control Power Modulator
circuits supply
bleeder divider
bleeder temperature The operating temperature block diagram
in a bleeder. It is generally high because of power (of a radio transmitter)
dissipation in the form of heat.
bleeding whites A flowing of the white areas of a
television picture into the black areas; an over- blocked impedance The input impedance of a
load condition. transducer, whose output load is a theoretically
blemish See BURN. infinite impedance.
blind flight The flying of aircraft entirely by means blockette In a computer, the subdivision of a char-
of instruments and electronic communications. acter block that is handled as a unit during data
blind landing Landing of an aircraft entirely by transfer.
means of instruments and electronic commnica- blocking action Obstruction of circuit action, usu-
tions. ally abrupt, through internal action or by the
blind zone 1. In radar operations, an area that gives application of an external signal. Thus, the
no echoes. 2. Skip zone (see ZONE OF SILENCE). operation of an amplifier can be blocked (output
blip 1. The pulse-like figure on a radar scan, indi- reduced to zero) by an input signal or by exces-
cating the transmission or reflection (see A-SCAN sive feedback, either of which overloads the
and J-SCAN). Also called PIP. 2. In visual align- input.
ment of a tuned circuit using a sweep generator blocking capacitor A capacitor inserted into a cir-
and marker generator, the pulse or dot produced cuit to prevent the passage of direct current while
on the response curve by the marker signal. 3. A easily passing alternating current.
short, momentary signal pulse, such as a single blocking choke Any inductor, such as a choke
Morse dot. coil, that is used to prevent the flow of an alter-
BLIP Abbreviation for background-limited infrared nating current while allowing direct current to
photoconductor. pass with little resistance.
blip-scan ratio The number of radar scans neces- blocking interference Radio interference from sig-
sary to show a visible blip, or echo, on a radar nals strong enough to reduce the receiver output
screen. through blocking action.