Page 98 - The Illustrated Dictionary of Electronics
P. 98
5059F-pB_56-92 4/9/01 4:45 PM Page 83
bow-tie test • brass pounder 83
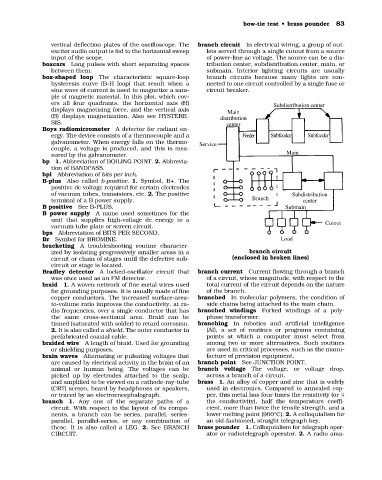
vertical deflection plates of the oscilloscope. The branch circuit In electrical wiring, a group of out-
exciter audio output is fed to the horizontal sweep lets served through a single cutout from a source
input of the scope. of power-line ac voltage. The source can be a dis-
boxcars Long pulses with short separating spaces tribution center, subdistribution center, main, or
between them. submain. Interior lighting circuits are usually
box-shaped loop The characteristic square-loop branch circuits because many lights are con-
hysteresis curve (B-H loop) that result when a nected to one circuit controlled by a single fuse or
sine wave of current is used to magnetize a sam- circuit breaker.
ple of magnetic material. In this plot, which cov-
ers all four quadrants, the horizontal axis (H) Subdistribution center
displays magnetizing force, and the vertical axis Main
(B) displays magnetization. Also see HYSTERE- distribution
SIS. center
Boys radiomicrometer A detector for radiant en-
ergy. The device consists of a thermocouple and a Feeder Subfeeder Subfeeder
galvanometer. When energy falls on the thermo- Service
couple, a voltage is produced, and this is mea-
sured by the galvanometer. Main
bp 1. Abbreviation of BOILING POINT. 2. Abbrevia-
tion of BANDPASS.
bpi Abbreviation of bits per inch.
B-plus Also called b-positive. 1. Symbol, B+. The
positive dc voltage required for certain electrodes
of vacuum tubes, transistors, etc. 2. The positive Subdistribution
terminal of a B power supply. Branch center
B positive See B-PLUS. Submain
B power supply A name used sometimes for the
unit that supplies high-voltage dc energy to a Cutout
vacuum tube plate or screen circuit.
bps Abbreviation of BITS PER SECOND.
Br Symbol for BROMINE. Load
bracketing A troubleshooting routine character-
ized by isolating progressively smaller areas in a branch circuit
circuit or chain of stages until the defective sub- (enclosed in broken lines)
circuit or stage is located.
Bradley detector A locked-oscillator circuit that branch current Current flowing through a branch
was once used as an FM detector. of a circuit, whose magnitude, with respect to the
braid 1. A woven network of fine metal wires used total current of the circuit depends on the nature
for grounding purposes. It is usually made of fine of the branch.
copper conductors. The increased surface-area- branched In molecular polymers, the condition of
to-volume ratio improves the conductivity, at ra- side chains being attached to the main chain.
dio frequencies, over a single conductor that has branched windings Forked windings of a poly-
the same cross-sectional area. Braid can be phase transformer.
tinned (saturated with solder) to retard corrosion. branching In robotics and artificial intelligence
2. It is also called a shield. The outer conductor in (AI), a set of routines or programs containing
prefabricated coaxial cable. points at which a computer must select from
braided wire A length of braid. Used for grounding among two or more alternatives. Such routines
or shielding purposes. are used in critical processes, such as the manu-
brain waves Alternating or pulsating voltages that facture of precision equipment.
are caused by electrical activity in the brain of an branch point See JUNCTION POINT.
animal or human being. The voltages can be branch voltage The voltage, or voltage drop,
picked up by electrodes attached to the scalp, across a branch of a circuit.
and amplified to be viewed on a cathode-ray-tube brass 1. An alloy of copper and zinc that is widely
(CRT) screen, heard by headphones or speakers, used in electronics. Compared to annealed cop-
1
or traced by an electroencephalograph. per, this metal has four times the resistivity (or ⁄4
branch 1. Any one of the separate paths of a the conductivity), half the temperature coeffi-
circuit. With respect to the layout of its compo- cient, more than twice the tensile strength, and a
nents, a branch can be series, parallel, series- lower melting point (900°C). 2. A colloquialism for
parallel, parallel-series, or any combination of an old-fashioned, straight telegraph key.
these. It is also called a LEG. 2. See BRANCH brass pounder 1. Colloquialism for telegraph oper-
CIRCUIT. ator or radiotelegraph operator. 2. A radio ama-