Page 97 - The Illustrated Dictionary of Electronics
P. 97
5059F-pB_56-92 4/9/01 4:45 PM Page 82
82 booster battery • bow-tie test
booster battery 1. A battery used to forward bias a program that is used to establish an alternate
diode detector into a favorable region of its con- version of the program.
duction curve, or to bias a bolometer into the borax-aluminum cell An electrolytic cell that con-
square-law region of its response. 2. A battery sists essentially of an aluminum electrode and a
supplying power to a booster. lead electrode in a saturated solution of sodium
booster gain The amplification (usually in terms of tetraborate (borax). After electroforming, such a
voltage gain) provided by a booster (see especially cell can be used either as a rectifier or as an elec-
BOOSTER, 2). trolytic capacitor.
boot 1. The powering-up routine in a digital com- boric acid Formula, H 3BO 3. A compound used var-
puter, in which the machine executes a series of iously in electronics—especially as the electrolyte
programs to get itself ready for use. 2. The in electrolytic capacitors.
resetting of a computer, by pressing certain key- bornite Formula, Cu 5FeS 4. A natural mineral that
board keys (e.g., CTRL-ALT-DEL), pressing a re- is a sulfide of copper and iron. Its crystalline
set button, or by powering-down, waiting about structure made it important in early semiconduc-
two minutes, and then powering-up again. 3. To tor diodes (crystal detectors).
install a computer diskette and instruct the com- boron Symbol, B. A metalloidal element. Atomic
puter to execute one or more programs on the number, 5. Atomic weight, 10.82. It is used as a
diskette. 4. A usually flexible protective nipple or dopant in semiconductor processing.
jacket pulled over a cable or connector, so called bot 1. Abbreviation for beginning of tape. 2. Abbre-
from its resemblance to a foot boot. viation of bottom.
boot loader A form of computer program that op- bottoming Excessive movement of the cone of a
erates on the BOOTSTRAP ROUTINE. loudspeaker or the diaphragm of a headphone so
bootstrap A technique for making a device or pro- that the magnet or supporting structure is struck
cess achieve a condition through its own actions; by the moving-coil piston assembly. It produces a
see BOOTSTRAP CIRCUIT, for example. clapping sound, particularly on bass (low-
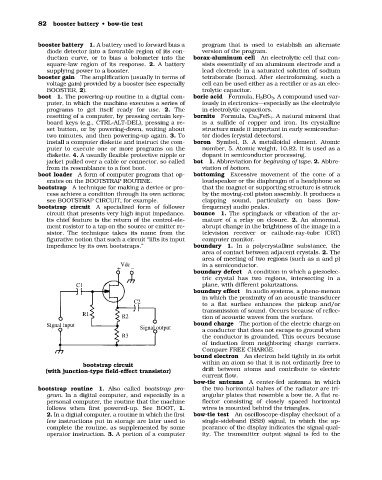
bootstrap circuit A specialized form of follower frequency) audio peaks.
circuit that presents very high input impedance. bounce 1. The springback or vibration of the ar-
Its chief feature is the return of the control-ele- mature of a relay on closure. 2. An abnormal,
ment resistor to a tap on the source or emitter re- abrupt change in the brightness of the image in a
sistor. The technique takes its name from the television receiver or cathode-ray-tube (CRT)
figurative notion that such a circuit “lifts its input computer monitor.
impedance by its own bootstraps.” boundary 1. In a polycrystalline substance, the
area of contact between adjacent crystals. 2. The
area of meeting of two regions (such as n and p)
Vdc in a semiconductor.
+ −
boundary defect A condition in which a piezoelec-
tric crystal has two regions, intersecting in a
C1 plane, with different polarizations.
boundary effect In audio systems, a pheno-menon
in which the proximity of an acoustic transducer
C2
to a flat surface enhances the pickup and/or
transmission of sound. Occurs because of reflec-
R1
R2 tion of acoustic waves from the surface.
Signal input bound charge The portion of the electric charge on
Signal output
a conductor that does not escape to ground when
R3 the conductor is grounded. This occurs because
of induction from neighboring charge carriers.
Compare FREE CHARGE.
bound electron An electron held tightly in its orbit
bootstrap circuit within an atom so that it is not ordinarily free to
(with junction-type field-effect transistor) drift between atoms and contribute to electric
current flow.
bow-tie antenna A center-fed antenna in which
bootstrap routine 1. Also called bootstrap pro- the two horizontal halves of the radiator are tri-
gram. In a digital computer, and especially in a angular plates that resemble a bow tie. A flat re-
personal computer, the routine that the machine flector consisting of closely spaced horizontal
follows when first powered-up. See BOOT, 1. wires is mounted behind the triangles.
2. In a digital computer, a routine in which the first bow-tie test An oscilloscope-display checkout of a
few instructions put in storage are later used to single-sideband (SSB) signal, in which the ap-
complete the routine, as supplemented by some pearance of the display indicates the signal qual-
operator instruction. 3. A portion of a computer ity. The transmitter output signal is fed to the