Page 11 - The Jet Engine
P. 11
1: Basic mechanics
Contents Page
Introduction 1
Principles of jet propulsion 2
Methods of jet propulsion 3
INTRODUCTION
1. The development of the gas turbine engine as an
aircraft power plant has been so rapid that it is
difficult to appreciate that prior to the 1950s very few
people had heard of this method of aircraft
propulsion. The possibility of using a reaction jet had
interested aircraft designers for a long time, but
initially the low speeds of early aircraft and the
unsuitably of a piston engine for producing the large
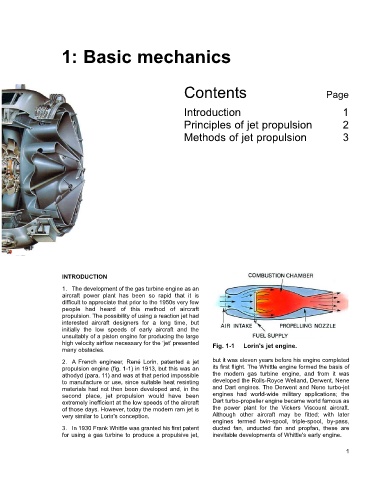
high velocity airflow necessary for the jet presented Fig. 1-1 Lorin's jet engine.
many obstacles.
2. A French engineer, René Lorin, patented a jet but it was eleven years before his engine completed
propulsion engine (fig. 1-1) in 1913, but this was an its first flight. The Whittle engine formed the basis of
athodyd (para. 11) and was at that period impossible the modern gas turbine engine, and from it was
to manufacture or use, since suitable heat resisting developed the Rolls-Royce Welland, Derwent, Nene
materials had not then been developed and, in the and Dart engines. The Derwent and Nene turbo-jet
second place, jet propulsion would have been engines had world-wide military applications; the
extremely inefficient at the low speeds of the aircraft Dart turbo-propeller engine became world famous as
of those days. However, today the modern ram jet is the power plant for the Vickers Viscount aircraft.
very similar to Lorin's conception. Although other aircraft may be fitted; with later
engines termed twin-spool, triple-spool, by-pass,
3. In 1930 Frank Whittle was granted his first patent ducted fan, unducted fan and propfan, these are
for using a gas turbine to produce a propulsive jet, inevitable developments of Whittle's early engine.
1