Page 13 - The Jet Engine
P. 13
Basic mechanics
velocity. In practice the former is preferred, since by
lowering the jet velocity relative to the atmosphere a
higher propulsive efficiency is obtained.
METHODS OF JET PROPULSION
10. The types of jet engine, whether ram jet, pulse
jet, rocket, gas turbine, turbo/ram jet or turbo-rocket,
differ only in the way in which the 'thrust provider', or
engine, supplies and converts the energy into power
for flight.
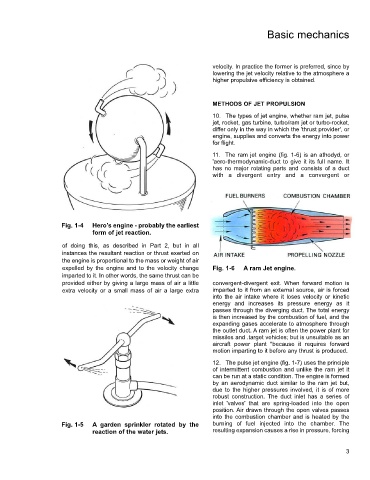
11. The ram jet engine (fig. 1-6) is an athodyd, or
'aero-thermodynamic-duct to give it its full name. It
has no major rotating parts and consists of a duct
with a divergent entry and a convergent or
Fig. 1-4 Heros engine - probably the earliest
form of jet reaction.
of doing this, as described in Part 2, but in all
instances the resultant reaction or thrust exerted on
the engine is proportional to the mass or weight of air
expelled by the engine and to the velocity change Fig. 1-6 A ram Jet engine.
imparted to it. In other words, the same thrust can be
provided either by giving a large mass of air a little convergent-divergent exit. When forward motion is
extra velocity or a small mass of air a large extra imparted to it from an external source, air is forced
into the air intake where it loses velocity or kinetic
energy and increases its pressure energy as it
passes through the diverging duct. The total energy
is then increased by the combustion of fuel, and the
expanding gases accelerate to atmosphere through
the outlet duct. A ram jet is often the power plant for
missiles and .target vehicles; but is unsuitable as an
aircraft power plant "because it requires forward
motion imparting to it before any thrust is produced.
12. The pulse jet engine (fig. 1-7) uses the principle
of intermittent combustion and unlike the ram jet it
can be run at a static condition. The engine is formed
by an aerodynamic duct similar to the ram jet but,
due to the higher pressures involved, it is of more
robust construction. The duct inlet has a series of
inlet 'valves' that are spring-loaded into the open
position. Air drawn through the open valves passes
into the combustion chamber and is heated by the
Fig. 1-5 A garden sprinkler rotated by the burning of fuel injected into the chamber. The
reaction of the water jets. resulting expansion causes a rise in pressure, forcing
3