Page 132 - The Jet Engine
P. 132
Starting and ignition
METHODS OF STARTING engine provides sufficient power for the engine
turbine to take over.
3. The starting procedure for all jet engines is
basically the same, but can be achieved by various Electric
methods. The type and power source for the starter 5. The electric starter is usually a direct current
varies in accordance with engine and aircraft require- (D.C.) electric motor coupled to the engine through a
ments. Some use electrical power, others use gas, reduction gear and ratchet mechanism, or clutch,
air or hydraulic pressure, and each has its own which automatically disengages after the engine has
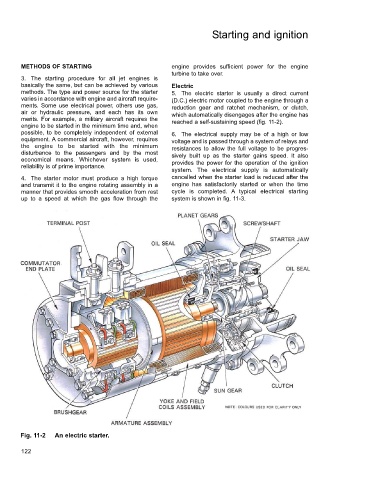
merits. For example, a military aircraft requires the reached a self-sustaining speed (fig. 11-2).
engine to be started in the minimum time and, when
possible, to be completely independent of external 6. The electrical supply may be of a high or low
equipment. A commercial aircraft, however, requires voltage and is passed through a system of relays and
the engine to be started with the minimum resistances to allow the full voltage to be progres-
disturbance to the passengers and by the most sively built up as the starter gains speed. It also
economical means. Whichever system is used, provides the power for the operation of the ignition
reliability is of prime importance.
system. The electrical supply is automatically
4. The starter motor must produce a high torque cancelled when the starter load is reduced after the
and transmit it to the engine rotating assembly in a engine has satisfactorily started or when the time
manner that provides smooth acceleration from rest cycle is completed. A typical electrical starting
up to a speed at which the gas flow through the system is shown in fig. 11-3.
Fig. 11-2 An electric starter.
122