Page 136 - The Jet Engine
P. 136
Starting and ignition
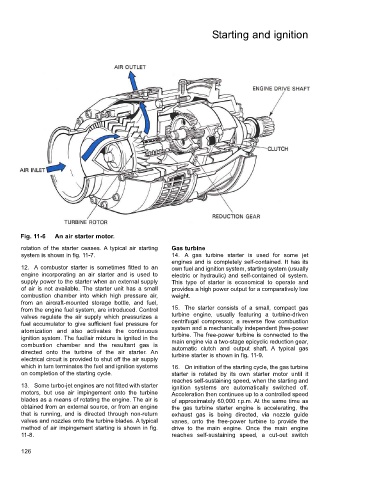
Fig. 11-6 An air starter motor.
rotation of the starter ceases. A typical air starting Gas turbine
system is shown in fig. 11-7. 14. A gas turbine starter is used for some jet
engines and is completely self-contained. It has its
12. A combustor starter is sometimes fitted to an own fuel and ignition system, starting system (usually
engine incorporating an air starter and is used to electric or hydraulic) and self-contained oil system.
supply power to the starter when an external supply This type of starter is economical to operate and
of air is not available. The starter unit has a small provides a high power output for a comparatively low
combustion chamber into which high pressure air, weight.
from an aircraft-mounted storage bottle, and fuel,
from the engine fuel system, are introduced. Control 15. The starter consists of a small, compact gas
valves regulate the air supply which pressurizes a turbine engine, usually featuring a turbine-driven
fuel accumulator to give sufficient fuel pressure for centrifugal compressor, a reverse flow combustion
atomization and also activates the continuous system and a mechanically independent |free-power
ignition system. The fuel/air mixture is ignited in the turbine. The free-power turbine is connected to the
main engine via a two-stage epicyclic reduction gear,
combustion chamber and the resultant gas is automatic clutch and output shaft. A typical gas
directed onto the turbine of the air starter. An turbine starter is shown in fig. 11-9.
electrical circuit is provided to shut off the air supply
which in turn terminates the fuel and ignition systems 16. On initiation of the starting cycle, the gas turbine
on completion of the starting cycle. starter is rotated by its own starter motor until it
reaches self-sustaining speed, when the starting and
13. Some turbo-jet engines are not fitted with starter ignition systems are automatically switched off.
motors, but use air impingement onto the turbine Acceleration then continues up to a controlled speed
blades as a means of rotating the engine. The air is of approximately 60,000 r.p.m. At the same time as
obtained from an external source, or from an engine the gas turbine starter engine is accelerating, the
that is running, and is directed through non-return exhaust gas is being directed, via nozzle guide
valves and nozzles onto the turbine blades. A typical vanes, onto the free-power turbine to provide the
method of air impingement starting is shown in fig. drive to the main engine. Once the main engine
11-8. reaches self-sustaining speed, a cut-out switch
126