Page 212 - The Jet Engine
P. 212
Noise suppression
produced by the reaction of each blade to the 9. Listed amongst the several other sources of
passage of air over its surface, even with a smooth noise within the engine is the combustion chamber. It
airstream. Turbulence in the airstream passing over is a significant but not a predominant source, due in
the blades increases the intensity of the broadband part to the fact that it is 'buried' in the core of the
noise and can also induce tones.
engine. Nevertheless it contributes to the broadband
7. With the pure jet engine the exhaust jet noise is noise, as a result of the violent activities which occur
of such a high level that the turbine and compressor within the combustion chamber.
noise is insignificant at all operating conditions,
except low landing-approach thrusts. With the by- METHODS OF SUPPRESSING NOISE
pass principle, the exhaust jet noise drops as the
velocity of the exhaust is reduced but the low 10. Noise suppression of internal sources is
pressure compressor and turbine noise increases approached in two ways; by basic design to minimize
due to the greater internal power handling. noise originating within or propagating from the
engine, and by the use of acoustically absorbent
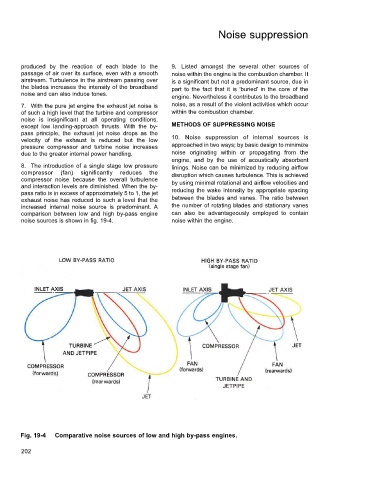
8. The introduction of a single stage low pressure linings. Noise can be minimized by reducing airflow
compressor (fan) significantly reduces the disruption which causes turbulence. This is achieved
compressor noise because the overall turbulence by using minimal rotational and airflow velocities and
and interaction levels are diminished. When the by-
pass ratio is in excess of approximately 5 to 1, the jet reducing the wake intensity by appropriate spacing
exhaust noise has reduced to such a level that the between the blades and vanes. The ratio between
increased internal noise source is predominant. A the number of rotating blades and stationary vanes
comparison between low and high by-pass engine can also be advantageously employed to contain
noise sources is shown in fig. 19-4. noise within the engine.
Fig. 19-4 Comparative noise sources of low and high by-pass engines.
202