Page 89 - The Jet Engine
P. 89
Lubrication
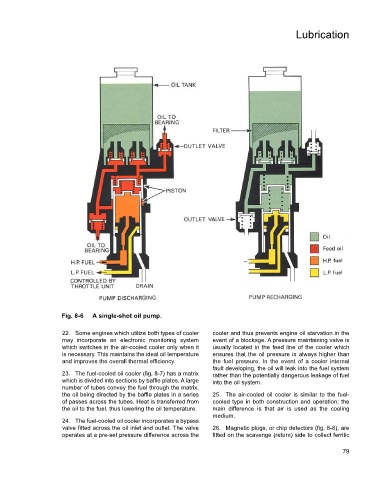
Fig. 8-6 A single-shot oil pump.
22. Some engines which utilize both types of cooler cooler and thus prevents engine oil starvation in the
may incorporate an electronic monitoring system event of a blockage. A pressure maintaining valve is
which switches in the air-cooled cooler only when it usually located in the feed line of the cooler which
is necessary. This maintains the ideal oil temperature ensures that the oil pressure is always higher than
and improves the overall thermal efficiency. the fuel pressure. In the event of a cooler internal
fault developing, the oil will leak into the fuel system
23. The fuel-cooled oil cooler (fig. 8-7) has a matrix rather than the potentially dangerous leakage of fuel
which is divided into sections by baffle plates. A large into the oil system.
number of tubes convey the fuel through the matrix,
the oil being directed by the baffle plates in a series 25. The air-cooled oil cooler is similar to the fuel-
of passes across the tubes. Heat is transferred from cooled type in both construction and operation; the
the oil to the fuel, thus lowering the oil temperature. main difference is that air is used as the cooling
medium.
24. The fuel-cooled oil cooler incorporates a bypass
valve fitted across the oil inlet and outlet. The valve 26. Magnetic plugs, or chip detectors (fig. 8-8), are
operates at a pre-set pressure difference across the fitted on the scavenge (return) side to collect ferritic
79