Page 203 - The Making of the German Post-war Economy
P. 203
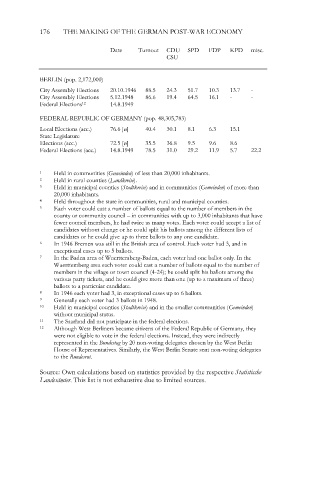
176 THE MAKING OF THE GERMAN POST-WAR ECONOMY
Date Turnout CDU SPD FDP KPD misc.
CSU
BERLIN (pop. 2,172,000)
City Assembly Elections 20.10.1946 88.5 24.3 51.7 10.3 13.7 -
City Assembly Elections 5.12.1948 86.6 19.4 64.5 16.1 - -
Federal Elections 12 14.8.1949
FEDERAL REPUBLIC OF GERMANY (pop. 48,305,783)
Local Elections (acc.) 76.6 [ø] 40.4 30.1 8.1 6.3 15.1
State Legislature
Elections (acc.) 72.5 [ø] 35.5 36.8 9.5 9.6 8.6
Federal Elections (acc.) 14.8.1949 78.5 31.0 29.2 11.9 5.7 22.2
1 Held in communities (Gemeinden) of less than 20,000 inhabitants.
2 Held in rural counties (Landkreise).
3 Held in municipal counties (Stadtkreise) and in communities (Gemeinden) of more than
20,000 inhabitants.
4 Held throughout the state in communities, rural and municipal counties.
5 Each voter could cast a number of ballots equal to the number of members in the
county or community council – in communities with up to 3,000 inhabitants that have
fewer council members, he had twice as many votes. Each voter could accept a list of
candidates without change or he could split his ballots among the different lists of
candidates or he could give up to three ballots to any one candidate.
6 In 1946 Bremen was still in the British area of control. Each voter had 3, and in
exceptional cases up to 5 ballots.
7 In the Baden area of Wuerttemberg-Baden, each voter had one ballot only. In the
Wuerttemberg area each voter could cast a number of ballots equal to the number of
members in the village or town council (4-24); he could split his ballots among the
various party tickets, and he could give more than one (up to a maximum of three)
ballots to a particular candidate.
8 In 1946 each voter had 3, in exceptional cases up to 6 ballots.
9 Generally each voter had 3 ballots in 1948.
10 Held in municipal counties (Stadtkreise) and in the smaller communities (Gemeinden)
without municipal status.
11 The Saarland did not participate in the federal elections.
12 Although West Berliners became citizens of the Federal Republic of Germany, they
were not eligible to vote in the federal elections. Instead, they were indirectly
represented in the Bundestag by 20 non-voting delegates chosen by the West Berlin
House of Representatives. Similarly, the West Berlin Senate sent non-voting delegates
to the Bundesrat.
Source: Own calculations based on statistics provided by the respective Statistische
Landesämter. This list is not exhaustive due to limited sources.