Page 135 - The Master Handbook Of Acoustics
P. 135
110 CHAPTER FIVE
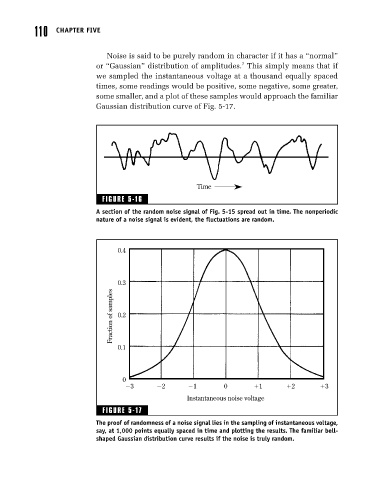
Noise is said to be purely random in character if it has a “normal”
7
or “Gaussian” distribution of amplitudes. This simply means that if
we sampled the instantaneous voltage at a thousand equally spaced
times, some readings would be positive, some negative, some greater,
some smaller, and a plot of these samples would approach the familiar
Gaussian distribution curve of Fig. 5-17.
Time
FIGURE 5-16
A section of the random noise signal of Fig. 5-15 spread out in time. The nonperiodic
nature of a noise signal is evident, the fluctuations are random.
0.4
0.3
Fraction of samples 0.2
0.1
0
3 2 1 0 1 2 3
Instantaneous noise voltage
FIGURE 5-17
The proof of randomness of a noise signal lies in the sampling of instantaneous voltage,
say, at 1,000 points equally spaced in time and plotting the results. The familiar bell-
shaped Gaussian distribution curve results if the noise is truly random.