Page 249 - The Master Handbook Of Acoustics
P. 249
224 CHAPTER NINE
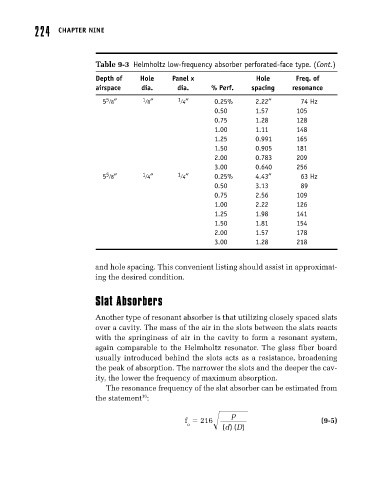
Table 9-3 Helmholtz low-frequency absorber perforated-face type. (Cont.)
Depth of Hole Panel x Hole Freq. of
airspace dia. dia. % Perf. spacing resonance
5 8″ 1 8″ 1 4″ 0.25% 2.22″ 74 Hz
5
0.50 1.57 105
0.75 1.28 128
1.00 1.11 148
1.25 0.991 165
1.50 0.905 181
2.00 0.783 209
3.00 0.640 256
5 8″ 1 4″ 1 4″ 0.25% 4.43″ 63 Hz
5
0.50 3.13 89
0.75 2.56 109
1.00 2.22 126
1.25 1.98 141
1.50 1.81 154
2.00 1.57 178
3.00 1.28 218
and hole spacing. This convenient listing should assist in approximat-
ing the desired condition.
Slat Absorbers
Another type of resonant absorber is that utilizing closely spaced slats
over a cavity. The mass of the air in the slots between the slats reacts
with the springiness of air in the cavity to form a resonant system,
again comparable to the Helmholtz resonator. The glass fiber board
usually introduced behind the slots acts as a resistance, broadening
the peak of absorption. The narrower the slots and the deeper the cav-
ity, the lower the frequency of maximum absorption.
The resonance frequency of the slat absorber can be estimated from
16
the statement :
p
f 216 (9-5)
o (d) (D)