Page 227 - The Six Sigma Project Planner
P. 227
Attribute Measurement Error Analysis
Attribute data consist of classifications rather than measurements. Attribute inspection
involves determining the classification of an item, e.g., is it “good” or “bad”? The
principles of good measurement for attribute inspection are the same as for measure-
ment inspection (Table 18). Thus, conceptually at least, it is possible to evaluate
attribute measurement systems in much the same way as we evaluate variables
measurement systems. Much less work has been done on evaluating attribute
measurement systems. The proposals provided in this book are those I’ve found to be
useful for my employers and clients. The ideas are not part of any standard and you are
encouraged to think about them critically before adopting them. I also include an
example of MINITAB’s attribute gauge R&R analysis.
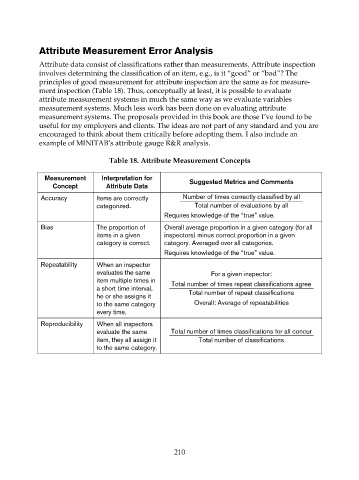
Table 18. Attribute Measurement Concepts
Measurement Interpretation for
Suggested Metrics and Comments
Concept Attribute Data
Accuracy Items are correctly Number of times correctly classified by all
categorized. Total number of evaluations by all
Requires knowledge of the “true” value.
Bias The proportion of Overall average proportion in a given category (for all
items in a given inspectors) minus correct proportion in a given
category is correct. category. Averaged over all categories.
Requires knowledge of the “true” value.
Repeatability When an inspector
evaluates the same For a given inspector:
item multiple times in
Total number of times repeat classifications agree
a short time interval,
he or she assigns it Total number of repeat classifications
to the same category Overall: Average of repeatabilities
every time.
Reproducibility When all inspectors
evaluate the same Total number of times classifications for all concur
item, they all assign it Total number of classifications
to the same category.
210