Page 138 - The Tribology Handbook
P. 138
A23
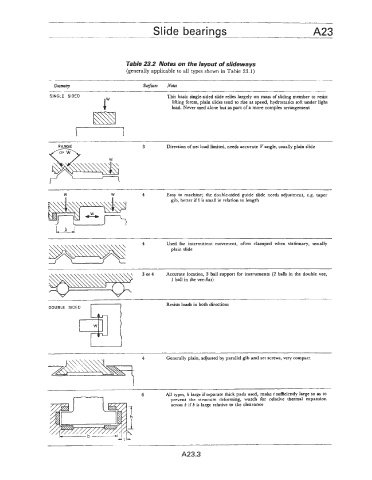
Table 23.2 Notes on the layout of slideways
(generally applicable to all types shown in Table 23.1)
&me@ Surfnces Notes
SINGLE SIDED This basic single-sided slide relies largely on mass of sliding member to resist
lifting forces, plain slides tend to rise at speed, hydrostatics soft under light
load. Never used alone but as part of a more complex arrangement
r 7
~~ ~
3 Direction of net load limited, needs accurate V angle, usually plain slide
W W 4 Easy to machine; the double-sided guide slide needs adjustment, e.g. taper
gib, better if b is small in relation to length
Used for intermittent movement, often clamped when stationary, usually
plain slide
~~~~
3 or 4 Accurate location, 3 ball support for instruments (2 balls in the double vee,
1 ball in the vee-flat)
DOUBLE SIDED I Resists loads in both directions
4 Generally plain, adjusted by parallel gib and set screws, very compact
6 All types, h large if separate thick pads used, make t sufficiently large so as to
I7 prevent the structure deforming, watch for relative thermal expansion
across b if b is large relative to the clearance
A23.3