Page 137 - The Tribology Handbook
P. 137
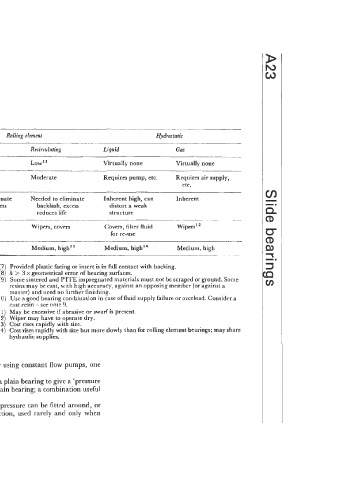
Table 23.1-continued
Plain Rolling element Hydrostatic
.- _--____
Metallmetal Plasticlmetal Non recirculating Recirculating Liguid Gas
_______ ____.~__.______
Wear rate Low/medium' I Low/medium" Low" Low" Virtually none Virtually none
- ~_____ ___________
Installation Easy Moderate Moderate Moderate Requires pump, etc. Requires air supply,
etc.
Preload used (on Negligible: it Negligible: it Needed to eliminate Needed to eliminate Inherent high, can Inherent
opposed faces) increases frictional increases frictional backlash, excess backlash, excess distort a weak
resistance resistance reduces life reduces life structure
-_--_I . -~ __ ~ ___.. _____~____
Protection required Wipers, covers Wipers," covers Wipers, covers Wipers, covers Covers, filter Huid Wipers"
ru for re-use
G3 ~~~~ __
Initial cost Low Low, medium Medium Medium, highI3 Medium, high14 Medium, high
(1) Fluid, at relatively high pressure is supplied to the shorter of the sliding members. (7) Provided plastic facing or insert is in full contact with backing.
(2) Typically 50 to 500 kN m-* for machine tools, otherwise use PV value for the material (8) h > 3 x geometrical error of bearing surfaces.
pair for boundary lubrication of a collar-type thrust bearing. (9) Some sintered and PTFE impregnated materials must not be scraped or ground. Some
(3) Ultimate, typically 0.5 X supply pressure X area; working fi 0.25 to 0.5 X ultimate. resins may be cast, with high accuracy, against an opposing member (or against a
(4) Limited, often, by air line pressure and area available. master) and need no further finishing.
(5) Prevent air entrainment by flooding the leading edge if the slide velocity exceeds the fluid (I 0) Use a good bearing combination in case of fluid supply failure or overload. Consider a
velocity in the direction of sliding. cast resin - see note 9.
(6) Ljable to stick-slip at velocities bslow 1 mm s-', use slideway oil with polar additive, (1 1) May be excessive if abrasive or swarfis present.
stiffen the drive so that (12) Wiper may have to operate dry.
[drive stiffness (N m -')/driven mass (kg)]) > 300 (13) Cost rises rapidly with size.
(14) Cost rises rapidly with size but more slowly than for rolling element bearings; may share
hydraulic supplies.
Combined bearings
Hydrostatic (liquid) bearings are usually controlled by a restrictor (as illustrated) or by using constant flow pumps, one
dedicated to each pocket.
Hydrostatic bearing style pockets supplied at constant pressure can be combined with a plain bearing to give a 'pressure
assist', Le., 'load relief, feature whilst still retaining the high stiffness characteristic of a plain bearing; a combination useful
for cases of heavy dead-weight loading.
Hydrostatic bearing style lands, supplied via small pockets at a usually low constant pressure can be fitted around, or
adjacent to, rolling element bearings to give improved damping in the transverse direction, used rarely and only when
vibration mode shape is suitable.