Page 311 - The Tribology Handbook
P. 311
Mineral oils c2
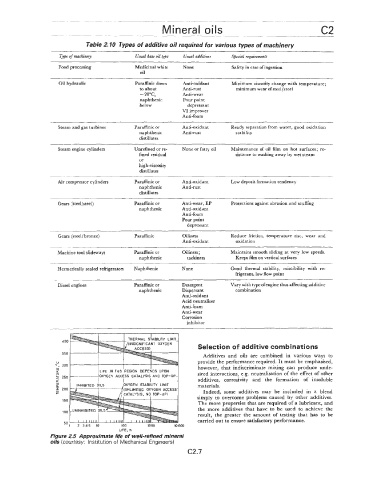
Table 2.10 Types of additive oil required for various types of machinery
~~
Type cf machinery Usual base oil tyfe Usual additives Special requirements
Food processing Medicinal white None Safety in case of ingestion
oil
Oil hydraulic Paraffinic down Anti-oxidant Minimum viscosity change with temperature;
to about Anti-rust minimum wear ofsteel/steel
- 20"C, Anti-wear
naphthenic Pour point
below depressant
VI improver
Anti-foam
Steam and gas turbines Paraffinic or Anti-oxidant Ready separation from water, good oxidation
naphthenic Anti-rust stability
distillates
Steam engine cylinders Unrefined or re- None or fatty oil Maintenance of oil film on hot surfaces; re-
fined residual sistance to washing away by wet steam
or
high-viscosity
distillates
Air compressor cylinders Paraffinic or Anti-oxidant Low deposit formation tendency
naphthenic Anti-rust
distillates
Gears (steel/steel) Paraffinic or Anti-wear, EP Protections against abrasion and scuffikg
naphthenic Anti-oxidant
Anti-foam
Pour point
depressant
Gears (steel / bronze) Paraffinic Oiliness Reduce friction, temperature rise, wear and
Anti-oxidant oxidation
Machine tool slideways Paraffinic or Oiliness ; Maintains smooth sliding at very low speeds.
naphthenic tackiness Keeps film on vertical surfaces
Hermetically sealed refrigerators Naphthenic None Good thermal stability, miscibility with re-
frigerant, low flow point
Diesel engines Paraffinic or Detergent Vary with type of engine thus affecting additive
naphthenic Dispersant combination
An ti-oxidan t
Acid neutraliser
An ti-foam
Anti-wear
Corrosion
inhibitor
400
Select ion of add it ive combinations
350
Additives and oils are combined in various ways to
U provide the performance required. It must be emphasised,
330
however, that indiscriminate mixing can produce unde-
LIFE IN THIS 'REGION DEPE~DS UPON
2 250 OXYGEN ACCESS CATALYSIS, AND TOP-UP sired interactions, e.g. neutralisation of the effect of other
z additives, corrosivity and the formation of insoluble
w OXYGEN STABILITY LIMIT
; 200 (UNLIMITED OXYGEN ACCESS materials.
+ Indeed, some additives may be included In a blend
simply to overcome problems caused by other additives.
150
The more properties that are required of a lubricant, and
the more additives that have to be used to achieve the
100
result, the greater the amount of testing that has to be
carried out to ensure satisfactory performance.
50
1 2 345 10 100 1000 10 000
LIFE, h
Figure 2.5 Approximate life of well-refined mineral
oils (courtesy: Institution of Mechanical Engineers)
C2.7