Page 233 - Welding of Aluminium and its Alloys
P. 233
Weld defects and quality control 213
geometry can all be identified, although planar defects normal to the beam
may not be detected.
To radiograph a welded joint a suitable source of radiation, a film in a
light-proof cassette and some method of processing the film are required.
This latter generally requires a dark room where the film can be developed,
fixed, washed, dried and viewed.The radiation can be produced from an X-
ray tube, the energy generally being described by the voltage and current
at which the tube is operated. These may vary from 20kV to 30MV and 10
to 30mA, although the normal limit for the commonly available industrial
units is around 400kV. A 400kV unit is capable of penetrating up to
100mm of steel and 200mm of aluminium. Gamma radiation is produced
by the decay of a naturally occurring or manufactured radioactive isotope.
The isotopes decay over a period of time, a measure of the longevity of the
source being the half life, the length of time taken for the source to decay
to half of its initial intensity. The most common isotopes are cobalt-60, half
life 5.3 years; caesium-137, half life 30 years; iridium-192, half life 74 days;
thulium-170, half life 127 days and ytterbium-169, half life 31 days. The
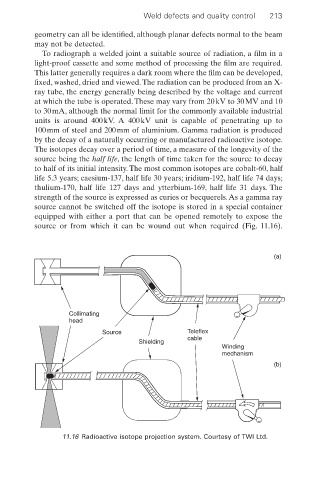
strength of the source is expressed as curies or becquerels.As a gamma ray
source cannot be switched off the isotope is stored in a special container
equipped with either a port that can be opened remotely to expose the
source or from which it can be wound out when required (Fig. 11.16).
(a)
Collimating
head
Source Teleflex
cable
Shielding
Winding
mechanism
(b)
11.16 Radioactive isotope projection system. Courtesy of TWI Ltd.