Page 38 - The Mechatronics Handbook
P. 38
TABLE 2.4 Generalized Through and Across Variables for Processes with Energy Flow
System Through Variables Across Variables
Electrical Electric current I Electric voltage U
Magnetic Magnetic Flow F Magnetic force Q
Mechanical
• translation Force F Velocity w
• rotation Torque M Rotationalspeed ω
Hydraulic Volume flow V ˙ Pressure p
Thermodynamic Entropy flow Temperature T
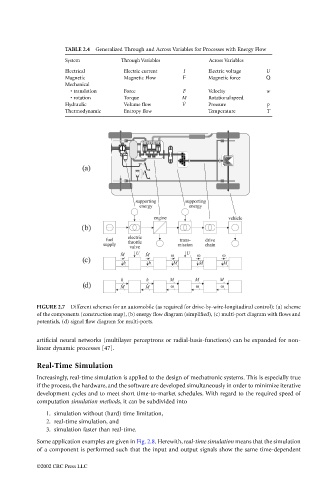
FIGURE 2.7 Different schemes for an automobile (as required for drive-by-wire-longitudinal control): (a) scheme
of the components (construction map), (b) energy flow diagram (simplified), (c) multi-port diagram with flows and
potentials, (d) signal flow diagram for multi-ports.
artificial neural networks (multilayer perceptrons or radial-basis-functions) can be expanded for non-
linear dynamic processes [47].
Real-Time Simulation
Increasingly, real-time simulation is applied to the design of mechatronic systems. This is especially true
if the process, the hardware, and the software are developed simultaneously in order to minimize iterative
development cycles and to meet short time-to-market schedules. With regard to the required speed of
computation simulation methods, it can be subdivided into
1. simulation without (hard) time limitation,
2. real-time simulation, and
3. simulation faster than real-time.
Some application examples are given in Fig. 2.8. Herewith, real-time simulation means that the simulation
of a component is performed such that the input and output signals show the same time-dependent
©2002 CRC Press LLC