Page 143 - Thermal Hydraulics Aspects of Liquid Metal Cooled Nuclear Reactors
P. 143
116 Thermal Hydraulics Aspects of Liquid Metal Cooled Nuclear Reactors
3.3.2.3 Some examples at KIT: The THEADES (LBE)
and KASOLA (Na) loops
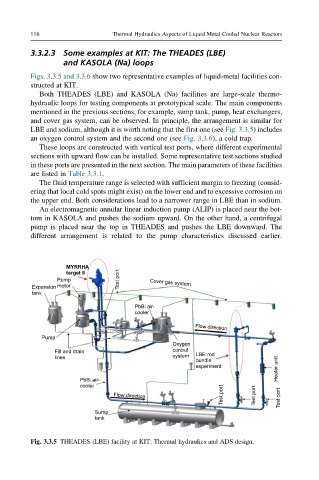
Figs. 3.3.5 and 3.3.6 show two representative examples of liquid-metal facilities con-
structed at KIT.
Both THEADES (LBE) and KASOLA (Na) facilities are large-scale thermo-
hydraulic loops for testing components at prototypical scale. The main components
mentioned in the previous sections, for example, sump tank, pump, heat exchangers,
and cover gas system, can be observed. In principle, the arrangement is similar for
LBE and sodium, although it is worth noting that the first one (see Fig. 3.3.5) includes
an oxygen control system and the second one (see Fig. 3.3.6), a cold trap.
These loops are constructed with vertical test ports, where different experimental
sections with upward flow can be installed. Some representative test sections studied
in these ports are presented in the next section. The main parameters of these facilities
are listed in Table 3.3.1.
The fluid temperature range is selected with sufficient margin to freezing (consid-
ering that local cold spots might exist) on the lower end and to excessive corrosion on
the upper end. Both considerations lead to a narrower range in LBE than in sodium.
An electromagnetic annular linear induction pump (ALIP) is placed near the bot-
tom in KASOLA and pushes the sodium upward. On the other hand, a centrifugal
pump is placed near the top in THEADES and pushes the LBE downward. The
different arrangement is related to the pump characteristics discussed earlier.
MYRRHA
target II
Pump Test port Cover gas system
Expansion motor
tank
PbBi air-
cooler
Flow direction
Pump
Oxygen
Fill and drain control LBE rod
lines system
bundle
experiment Heater unit
PbBi air-
cooler
Test port
Flow direction Test port Test port
Sump
tank
Fig. 3.3.5 THEADES (LBE) facility at KIT: Thermal hydraulics and ADS design.