Page 165 - Trenchless Technology Piping Installation and Inspection
P. 165
Pipe and Pipe Installation Considerations 131
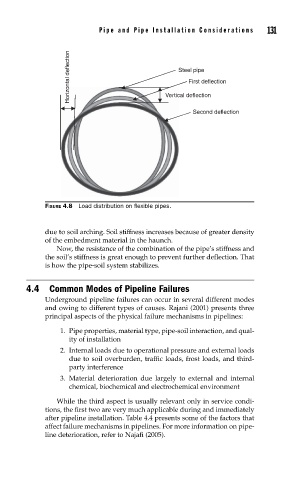
Horizontal deflection Steel pipe
First deflection
Vertical deflection
Second deflection
FIGURE 4.8 Load distribution on fl exible pipes.
due to soil arching. Soil stiffness increases because of greater density
of the embedment material in the haunch.
Now, the resistance of the combination of the pipe’s stiffness and
the soil’s stiffness is great enough to prevent further deflection. That
is how the pipe-soil system stabilizes.
4.4 Common Modes of Pipeline Failures
Underground pipeline failures can occur in several different modes
and owing to different types of causes. Rajani (2001) presents three
principal aspects of the physical failure mechanisms in pipelines:
1. Pipe properties, material type, pipe-soil interaction, and qual-
ity of installation
2. Internal loads due to operational pressure and external loads
due to soil overburden, traffic loads, frost loads, and third-
party interference
3. Material deterioration due largely to external and internal
chemical, biochemical and electrochemical environment
While the third aspect is usually relevant only in service condi-
tions, the first two are very much applicable during and immediately
after pipeline installation. Table 4.4 presents some of the factors that
affect failure mechanisms in pipelines. For more information on pipe-
line deterioration, refer to Najafi (2005).