Page 166 - Trenchless Technology Piping Installation and Inspection
P. 166
132 Cha pte r F o u r
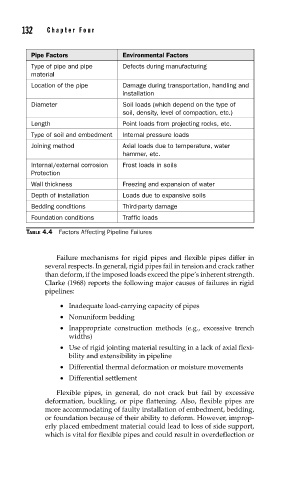
Pipe Factors Environmental Factors
Type of pipe and pipe Defects during manufacturing
material
Location of the pipe Damage during transportation, handling and
installation
Diameter Soil loads (which depend on the type of
soil, density, level of compaction, etc.)
Length Point loads from projecting rocks, etc.
Type of soil and embedment Internal pressure loads
Joining method Axial loads due to temperature, water
hammer, etc.
Internal/external corrosion Frost loads in soils
Protection
Wall thickness Freezing and expansion of water
Depth of installation Loads due to expansive soils
Bedding conditions Third-party damage
Foundation conditions Traffic loads
TABLE 4.4 Factors Affecting Pipeline Failures
Failure mechanisms for rigid pipes and flexible pipes differ in
several respects. In general, rigid pipes fail in tension and crack rather
than deform, if the imposed loads exceed the pipe’s inherent strength.
Clarke (1968) reports the following major causes of failures in rigid
pipelines:
• Inadequate load-carrying capacity of pipes
• Nonuniform bedding
• Inappropriate construction methods (e.g., excessive trench
widths)
• Use of rigid jointing material resulting in a lack of axial flexi-
bility and extensibility in pipeline
• Differential thermal deformation or moisture movements
• Differential settlement
Flexible pipes, in general, do not crack but fail by excessive
deformation, buckling, or pipe flattening. Also, flexible pipes are
more accommodating of faulty installation of embedment, bedding,
or foundation because of their ability to deform. However, improp-
erly placed embedment material could lead to loss of side support,
which is vital for flexible pipes and could result in overdeflection or