Page 30 - Trenchless Technology Piping Installation and Inspection
P. 30
New Pipeline Installations 5
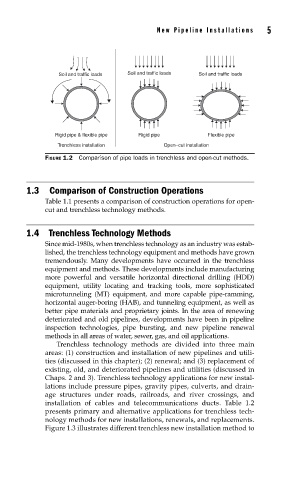
Soil and traffic loads Soil and traffic loads Soil and traffic loads
Rigid pipe & flexible pipe Rigid pipe Flexible pipe
Trenchless installation Open–cut installation
FIGURE 1.2 Comparison of pipe loads in trenchless and open-cut methods.
1.3 Comparison of Construction Operations
Table 1.1 presents a comparison of construction operations for open-
cut and trenchless technology methods.
1.4 Trenchless Technology Methods
Since mid-1980s, when trenchless technology as an industry was estab-
lished, the trenchless technology equipment and methods have grown
tremendously. Many developments have occurred in the trenchless
equipment and methods. These developments include manufacturing
more powerful and versatile horizontal directional drilling (HDD)
equipment, utility locating and tracking tools, more sophisticated
microtunneling (MT) equipment, and more capable pipe-ramming,
horizontal auger-boring (HAB), and tunneling equipment, as well as
better pipe materials and proprietary joints. In the area of renewing
deteriorated and old pipelines, developments have been in pipeline
inspection technologies, pipe bursting, and new pipeline renewal
methods in all areas of water, sewer, gas, and oil applications.
Trenchless technology methods are divided into three main
areas: (1) construction and installation of new pipelines and utili-
ties (discussed in this chapter); (2) renewal; and (3) replacement of
existing, old, and deteriorated pipelines and utilities (discussed in
Chaps. 2 and 3). Trenchless technology applications for new instal-
lations include pressure pipes, gravity pipes, culverts, and drain-
age structures under roads, railroads, and river crossings, and
installation of cables and telecommunications ducts. Table 1.2
presents primary and alternative applications for trenchless tech-
nology methods for new installations, renewals, and replacements.
Figure 1.3 illustrates different trenchless new installation method to