Page 33 - Trenchless Technology Piping Installation and Inspection
P. 33
8 Cha pte r O n e
Horizontal directional
Pressure pipes Water, gas and oil
drilling
Diameter Conventional pipe
range > jacking and
42 in. utility tunneling
Diameter
Sanity and storm
Gravity pipes range commonly Microtunneling
sewers for 12–42 in.
New installation
methods
Diameter Pilot-tube
range 4– microtunneling
30 in.
Horizontal auger
Road and railroad Pressure and
crossings gravity pipes boring and pipe
ramming
Cables and Mini-HDD and
telecommunications Conduits compaction methods
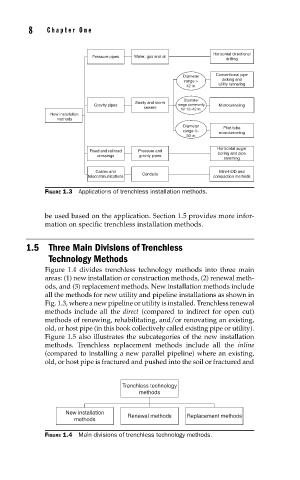
FIGURE 1.3 Applications of trenchless installation methods.
be used based on the application. Section 1.5 provides more infor-
mation on specific trenchless installation methods.
1.5 Three Main Divisions of Trenchless
Technology Methods
Figure 1.4 divides trenchless technology methods into three main
areas: (1) new installation or construction methods, (2) renewal meth-
ods, and (3) replacement methods. New installation methods include
all the methods for new utility and pipeline installations as shown in
Fig. 1.3, where a new pipeline or utility is installed. Trenchless renewal
methods include all the direct (compared to indirect for open cut)
methods of renewing, rehabilitating, and/or renovating an existing,
old, or host pipe (in this book collectively called existing pipe or utility).
Figure 1.5 also illustrates the subcategories of the new installation
methods. Trenchless replacement methods include all the inline
(compared to installing a new parallel pipeline) where an existing,
old, or host pipe is fractured and pushed into the soil or fractured and
Trenchless technology
methods
New installation Renewal methods Replacement methods
methods
FIGURE 1.4 Main divisions of trenchless technology methods.