Page 60 - Trenchless Technology Piping Installation and Inspection
P. 60
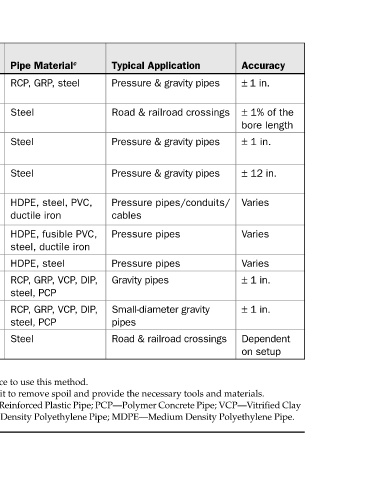
Accuracy ± 1 in. ± 1% of the bore length ± 1 in. ± 12 in. Varies Varies Varies ± 1 in. ± 1 in. Dependent on setup
Typical Application Pressure & gravity pipes Road & railroad crossings Pressure & gravity pipes Pressure & gravity pipes Pressure pipes/conduits/ cables Pressure pipes Pressure pipes Gravity pipes Small-diameter gravity pipes Road & railroad crossings
Pipe Material c RCP, GRP, steel Steel Steel Steel HDPE, steel, PVC, ductile iron HDPE, fusible PVC, steel, ductile iron HDPE, steel RCP, GRP, VCP, DIP, steel, PCP RCP, GRP, VCP, DIP, steel, PCP Steel
Depth (ft) b Maximum depths are dependent on practical capability of using a shaft or pit to remove spoil and provide the necessary tools and materials. c Steel—Steel Casing Pipe; RCP—Reinforced Concrete Pipe; GRP—Glass-Fiber Reinforced Plastic Pipe; PCP—Polymer Concret
Max N/A a N/A a N/A a N/A a 60 100 200 N/A b N/A b N/A b
Inst. Length (ft) 1600–3500 600 600 600 600 600–2000 2000–6000 1500 300 400 a Not all the contractors have the necessary equipment and required experience to use this method.
Diameter Range (in.) 42 & up (144 in.) 4–60 4–60 4–60 2–12 12–24 24–60 12–136 6–30 4–140 Main Characteristics of Trenchless Installation Methods
Trenchless Method Conventional pipe jacking & utility tunneling Auger boring (conventional) Auger boring steered on grade a Auger boring steered on + grade a Mini-HDD Midi-HDD Maxi-HDD Microtunneling Pilot tube microtunneling Pipe ramming TABLE 1.5
32 line