Page 61 - Trenchless Technology Piping Installation and Inspection
P. 61
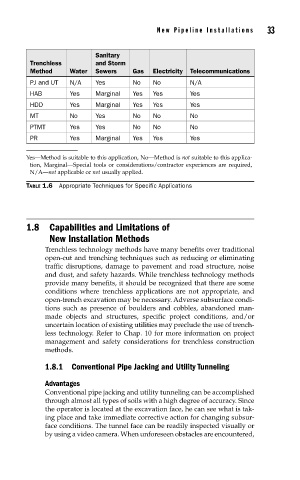
New Pipeline Installations 33
Sanitary
Trenchless and Storm
Method Water Sewers Gas Electricity Telecommunications
PJ and UT N/A Yes No No N/A
HAB Yes Marginal Yes Yes Yes
HDD Yes Marginal Yes Yes Yes
MT No Yes No No No
PTMT Yes Yes No No No
PR Yes Marginal Yes Yes Yes
Yes—Method is suitable to this application, No—Method is not suitable to this applica-
tion, Marginal—Special tools or considerations/contractor experiences are required,
N/A—not applicable or not usually applied.
TABLE 1.6 Appropriate Techniques for Specific Applications
1.8 Capabilities and Limitations of
New Installation Methods
Trenchless technology methods have many benefits over traditional
open-cut and trenching techniques such as reducing or eliminating
traffic disruptions, damage to pavement and road structure, noise
and dust, and safety hazards. While trenchless technology methods
provide many benefits, it should be recognized that there are some
conditions where trenchless applications are not appropriate, and
open-trench excavation may be necessary. Adverse subsurface condi-
tions such as presence of boulders and cobbles, abandoned man-
made objects and structures, specific project conditions, and/or
uncertain location of existing utilities may preclude the use of trench-
less technology. Refer to Chap. 10 for more information on project
management and safety considerations for trenchless construction
methods.
1.8.1 Conventional Pipe Jacking and Utility Tunneling
Advantages
Conventional pipe jacking and utility tunneling can be accomplished
through almost all types of soils with a high degree of accuracy. Since
the operator is located at the excavation face, he can see what is tak-
ing place and take immediate corrective action for changing subsur-
face conditions. The tunnel face can be readily inspected visually or
by using a video camera. When unforeseen obstacles are encountered,