Page 180 - Tribology in Machine Design
P. 180
166 Tribology in machine design
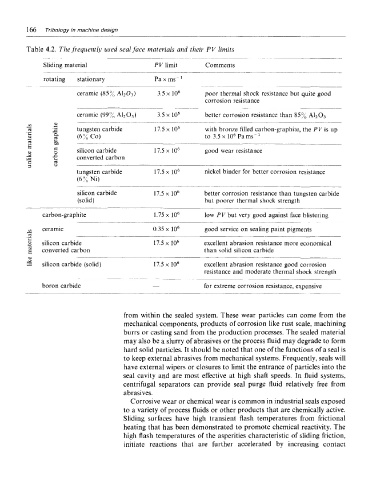
Table 4.2. The frequently used seal face materials and their PV limits
Sliding material PV limit Comments
rotating stationary Paxms" 1
ceramic (85% A1 2 O 3 ) 3.5 x 10 6 poor thermal shock resistance but quite good
corrosion resistance
ceramic (99% A1 2O 3) 3.5 x 10 6 better corrosion resistance than 85% A1 2O 3
tungsten carbide 17.5 x 10 6 with bronze filled carbon-graphite, the PV is up
(6% Co) to 3.5 x IC^Pams- 1
silicon carbide 17.5 x 10 6 good wear resistance
converted carbon
tungsten carbide 17.5 x 10 6 nickel binder for better corrosion resistance
(6%Ni)
silicon carbide 17.5 x 10 6 better corrosion resistance than tungsten carbide
(solid) but poorer thermal shock strength
carbon-graphite 1.75 x 10 low PV but very good against face blistering
ceramic 0.35 x 10 6 good service on sealing paint pigments
silicon carbide 17.5 x 10 6 excellent abrasion resistance more economical
converted carbon than solid silicon carbide
silicon carbide (solid) 17.5 x 10 6 excellent abrasion resistance good corrosion
resistance and moderate thermal shock strength
boron carbide — for extreme corrosion resistance, expensive
from within the sealed system. These wear particles can come from the
mechanical components, products of corrosion like rust scale, machining
burrs or casting sand from the production processes. The sealed material
may also be a slurry of abrasives or the process fluid may degrade to form
hard solid particles. It should be noted that one of the functions of a seal is
to keep external abrasives from mechanical systems. Frequently, seals will
have external wipers or closures to limit the entrance of particles into the
seal cavity and are most effective at high shaft speeds. In fluid systems,
centrifugal separators can provide seal purge fluid relatively free from
abrasives.
Corrosive wear or chemical wear is common in industrial seals exposed
to a variety of process fluids or other products that are chemically active.
Sliding surfaces have high transient flash temperatures from frictional
heating that has been demonstrated to promote chemical reactivity. The
high flash temperatures of the asperities characteristic of sliding friction,
initiate reactions that are further accelerated by increasing contact