Page 267 - Tunable Lasers Handbook
P. 267
6 Transition Metal Solid-state Lasers 227
3T4
\
Central Mutual Crystal Spin
Potential Repulsion Field Orbit
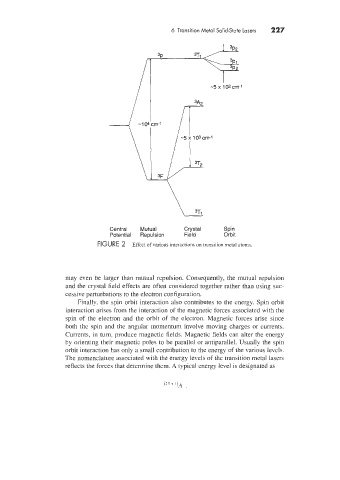
FIGURE 2 Effect of various interactions on transition metal atoms.
may even be larger than mutual repulsion. Consequently, the mutgal repulsion
and the crystal field effects are often considered together rather than using suc-
cessive perturbations to the electron configuration.
Finally. the spin orbit interaction also contributes to the energy. Spin orbit
interaction arises from the interaction of the magnetic forces associated with the
spin of the electron and the orbit of the electron. Magnetic forces arise since
both the spin and the angular momentum involve moving charges or currents.
Currents, in turn. produce magnetic fields. Magnetic fields can alter the energy
by orienting their magnetic poles to be parallel or antiparallel. Usually the spin
orbit interaction has only a small contribution to the energy of the various levels.
The nomenclature associated with the energy levels of the transition metal lasers
reflects the forces that determine them. A typical energy level is designated as