Page 294 - Tunable Lasers Handbook
P. 294
254 Norman P. Barnes
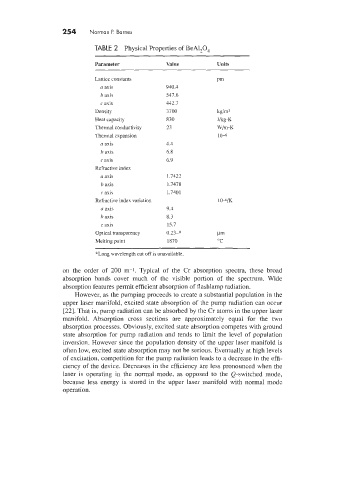
TABLE 2 Physical Properties of BeA1,0,
Parameter Value Units
Lattice constants Pm
a axis 940.1
h axis 547.6
c axis 112.7
Density 3700 hg/m'
Heat capacity 830 Jkg-K
Thermal conductivity 23 1VIm-K
Thermal expansion 10-6
a axis 1.4
b anis 6.8
c axis 6.9
Refracti\Fe index
a axis 1.7421
b axis 1.7478
c axis 1.7401
Refractive index variation 10-6K
a axis 9.1
b anis 8.3
c axis 15.7
Optical transparency 0.23-* Pm
Melting point 1870 "C
*Long wavelength cut off is unavailable.
on the order of 200 m-1. Typical of the Cr absorption spectra, these broad
absorption bands cover much of the visible portion of the spectrum. Wide
absorption features permit efficient absorption of flashlamp radiation.
However, as the pumping proceeds to create a substantial population in the
upper laser manifold, excited state absorption of the pump radiation can occur
[22]. That is, pump radiation can be absorbed by the Cr atoms in the upper laser
manifold. Absorption cross sections are approximately equal for the two
absorption processes. Obviously, excited state absorption competes with ground
state absorption for pump radiation and tends to limit the level of population
inversion. However since the population density of the upper laser manifold is
often low, excited state absorption may not be serious. Eventually at high levels
of excitation, competition for the pump radiation leads to a decrease in the effi-
ciency of the device. Decreases in the efficiency are less pronounced when the
laser is operating in the normal mode, as opposed to the Q-switched mode,
because less energy is stored in the upper laser manifold with normal mode
operation.