Page 85 - Tunable Lasers Handbook
P. 85
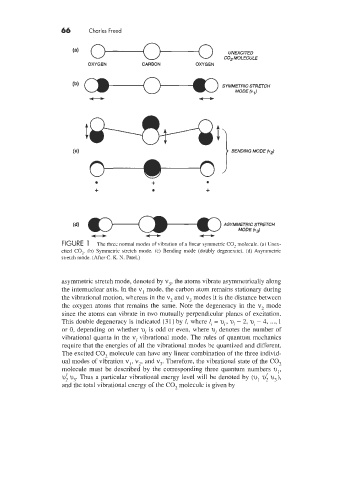
66 Charles Freed
UNEXCITED
COP MOLECULE
OXYGEN CARBON OXYGEN
(4 } BENDING MODE (v2)
+
+ +
- ASYMMETRIC (bd STRETCH
MODE
U
FIGURE 1 The three normal modes of vibration of a linear symmetric C02 molecule. (a) Unex-
cited CO,. (b) Symmemc stretch mode. (c) Bending mode (doubly degenerate). (d) Asymmetric
stretch mode. (After C. K N. Patel.)
asymmetric stretch mode, denoted by v;. the atoms vibrate asymmetrically along
the internuclear axis. In the v1 mode, the carbon atom remains stationary during
the vibrational motion, whereas in the v, and v; modes it is the distance between
the oxygen atoms that remains the same. Note the degeneracy in the v, mode
since the atoms can vibrate in two mutually perpendicular planes of excitation.
This double degeneracy is indicated [31] by 1, where lI = u,, u2 - 2. u, - 4, ..., 1
or 0. depending on whether uf is odd or even. where uf denotes the number of
vibrational quanta in the vf vibrational mode. The rules of quantum mechanics
require that the energies of all the vibrational modes be quantized and different.
The excited CO, molecule can have any linear combination of the three individ-
ual modes of vibration vl. v2, and v3. Therefore, the vibrational state of the CO, I
molecule must be described by the corresponding three quantum numbers ul,
u3. Thus a particular vibrational energy level will be denoted by (ul us u3),
and the total vibrational energy of the CO, molecule is given by