Page 101 - Understanding Automotive Electronics
P. 101
2735 | CH 3 Page 88 Tuesday, March 10, 1998 11:03 AM
3 ELECTRONICS FUNDAMENTALS
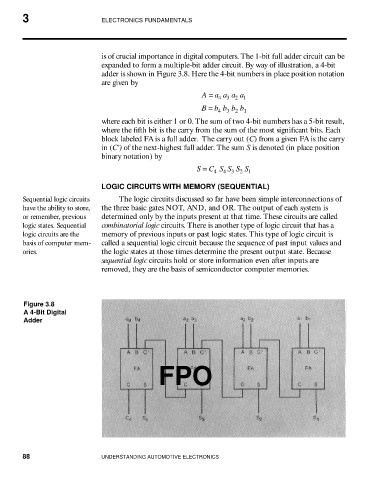
is of crucial importance in digital computers. The 1-bit full adder circuit can be
expanded to form a multiple-bit adder circuit. By way of illustration, a 4-bit
adder is shown in Figure 3.8. Here the 4-bit numbers in place position notation
are given by
A = a a a a
4 3 2 1
B = b b b b 1
3
2
4
where each bit is either 1 or 0. The sum of two 4-bit numbers has a 5-bit result,
where the fifth bit is the carry from the sum of the most significant bits. Each
block labeled FA is a full adder. The carry out (C) from a given FA is the carry
in (C') of the next-highest full adder. The sum S is denoted (in place position
binary notation) by
S = C S S S S 1
2
4 4 3
LOGIC CIRCUITS WITH MEMORY (SEQUENTIAL)
Sequential logic circuits The logic circuits discussed so far have been simple interconnections of
have the ability to store, the three basic gates NOT, AND, and OR. The output of each system is
or remember, previous determined only by the inputs present at that time. These circuits are called
logic states. Sequential combinatorial logic circuits. There is another type of logic circuit that has a
logic circuits are the memory of previous inputs or past logic states. This type of logic circuit is
basis of computer mem- called a sequential logic circuit because the sequence of past input values and
ories. the logic states at those times determine the present output state. Because
sequential logic circuits hold or store information even after inputs are
removed, they are the basis of semiconductor computer memories.
Figure 3.8
A 4-Bit Digital
Adder
FPO
88 UNDERSTANDING AUTOMOTIVE ELECTRONICS