Page 191 - Understanding Automotive Electronics
P. 191
2735 | CH 5 Page 178 Tuesday, March 10, 1998 11:10 AM
5 THE BASICS OF ELECTRONIC ENGINE CONTROL
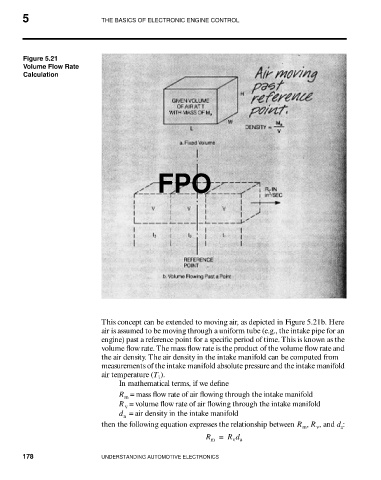
Figure 5.21
Volume Flow Rate
Calculation
FPO
This concept can be extended to moving air, as depicted in Figure 5.21b. Here
air is assumed to be moving through a uniform tube (e.g., the intake pipe for an
engine) past a reference point for a specific period of time. This is known as the
volume flow rate. The mass flow rate is the product of the volume flow rate and
the air density. The air density in the intake manifold can be computed from
measurements of the intake manifold absolute pressure and the intake manifold
air temperature (T ).
i
In mathematical terms, if we define
R = mass flow rate of air flowing through the intake manifold
m
R = volume flow rate of air flowing through the intake manifold
v
d = air density in the intake manifold
a
then the following equation expresses the relationship between R , R , and d :
v
m
a
R m = R d
v a
178 UNDERSTANDING AUTOMOTIVE ELECTRONICS