Page 46 - Understanding Automotive Electronics
P. 46
2735 | CH 2 Page 33 Tuesday, March 10, 1998 10:55 AM
THE SYSTEMS APPROACH TO CONTROL AND INSTRUMENTATION 2
to a proportional electrical signal continuously. That is, as the input quantity
varies, the sensor output voltage varies proportionately. In mathematical terms,
letting x be the amplitude of the input quantity (e.g., pressure, displacement, or
temperature), the output voltage of an ideal sensor (denoted v) is continuously
proportional to x :
v = k x
s
In this expression, k represents the so-called transducer gain of the sensor.
s
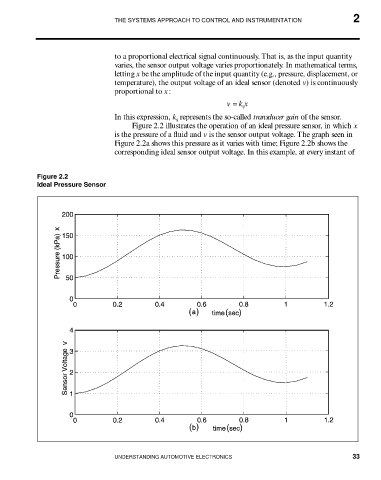
Figure 2.2 illustrates the operation of an ideal pressure sensor, in which x
is the pressure of a fluid and v is the sensor output voltage. The graph seen in
Figure 2.2a shows this pressure as it varies with time; Figure 2.2b shows the
corresponding ideal sensor output voltage. In this example, at every instant of
Figure 2.2
Ideal Pressure Sensor
UNDERSTANDING AUTOMOTIVE ELECTRONICS 33