Page 264 -
P. 264
Q6-6 How Can Organizations Use Cloud Services Securely?
Q6-6 How Can Organizations Use Cloud Services 263
Securely?
The Internet and cloud services based on Internet infrastructure provide powerful processing
and storage services at a fraction of the cost of private data centers. However, the Internet is a
jungle of threats to data and computing infrastructure, as discussed in Chapter 10. How can
organizations realize the benefits of cloud technology without succumbing to those threats?
The answer involves a combination of technologies that we will address, at a very high
level, in this question. As you read, realize that no security story is ever over; attackers con-
stantly strive to find ways around security safeguards, and occasionally they succeed. Thus, you
can expect that cloud security will evolve beyond that described here throughout your career.
We begin with a discussion of VPNs, a technology used to provide secure communication over
the Internet.
Virtual Private Networks (VPNs)
A virtual private network (VPN) uses the Internet to create the appearance of private, secure
connections. In the IT world, the term virtual means something that appears to exist but in fact
does not. Here, a VPN uses the public Internet to create the appearance of a private connection on
a secure network.
A Typical VPN
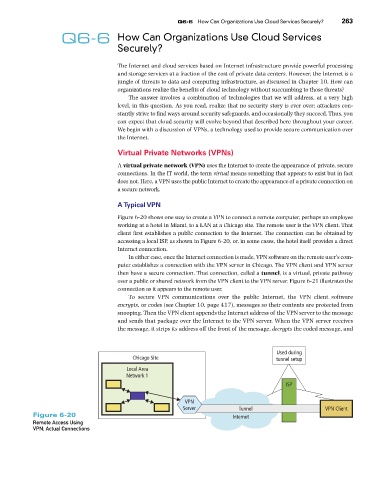
Figure 6-20 shows one way to create a VPN to connect a remote computer, perhaps an employee
working at a hotel in Miami, to a LAN at a Chicago site. The remote user is the VPN client. That
client first establishes a public connection to the Internet. The connection can be obtained by
accessing a local ISP, as shown in Figure 6-20, or, in some cases, the hotel itself provides a direct
Internet connection.
In either case, once the Internet connection is made, VPN software on the remote user’s com-
puter establishes a connection with the VPN server in Chicago. The VPN client and VPN server
then have a secure connection. That connection, called a tunnel, is a virtual, private pathway
over a public or shared network from the VPN client to the VPN server. Figure 6-21 illustrates the
connection as it appears to the remote user.
To secure VPN communications over the public Internet, the VPN client software
encrypts, or codes (see Chapter 10, page 417), messages so their contents are protected from
snooping. Then the VPN client appends the Internet address of the VPN server to the message
and sends that package over the Internet to the VPN server. When the VPN server receives
the message, it strips its address off the front of the message, decrypts the coded message, and
Used during
Chicago Site tunnel setup
Local Area
Network 1
ISP
VPN
Server Tunnel VPN Client
Figure 6-20 Internet
Remote Access Using
VPN; Actual Connections