Page 289 -
P. 289
Chapter 7 Processes, Organizations, and Information Systems
288
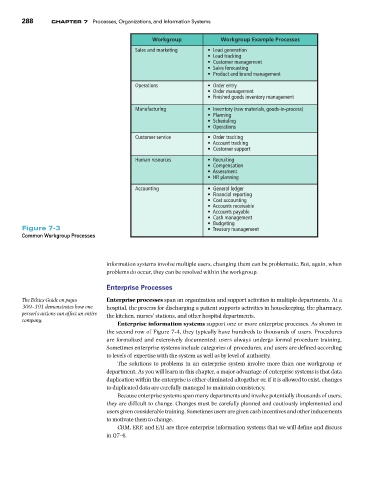
9QTMITQWR 9QTMITQWR 'ZCORNG 2TQEGUUGU
Sales and marketing • Lead generation
• Lead tracking
• Customer management
• Sales forecasting
• Product and brand management
Operations • Order entry
• Order management
• Finished goods inventory management
Manufacturing • Inventory (raw materials, goods-in-process)
• Planning
• Scheduling
• Operations
Customer service • Order tracking
• Account tracking
• Customer support
Human resources • Recruiting
• Compensation
• Assessment
• HR planning
Accounting • General ledger
• Financial reporting
• Cost accounting
• Accounts receivable
• Accounts payable
• Cash management
• Budgeting
Figure 7-3 • Treasury management
Common Workgroup Processes
information systems involve multiple users, changing them can be problematic. But, again, when
problems do occur, they can be resolved within the workgroup.
Enterprise Processes
The Ethics Guide on pages Enterprise processes span an organization and support activities in multiple departments. At a
300–301 demonstrates how one hospital, the process for discharging a patient supports activities in housekeeping, the pharmacy,
person’s actions can affect an entire the kitchen, nurses’ stations, and other hospital departments.
company.
Enterprise information systems support one or more enterprise processes. As shown in
the second row of Figure 7-4, they typically have hundreds to thousands of users. Procedures
are formalized and extensively documented; users always undergo formal procedure training.
Sometimes enterprise systems include categories of procedures, and users are defined according
to levels of expertise with the system as well as by level of authority.
The solutions to problems in an enterprise system involve more than one workgroup or
department. As you will learn in this chapter, a major advantage of enterprise systems is that data
duplication within the enterprise is either eliminated altogether or, if it is allowed to exist, changes
to duplicated data are carefully managed to maintain consistency.
Because enterprise systems span many departments and involve potentially thousands of users,
they are difficult to change. Changes must be carefully planned and cautiously implemented and
users given considerable training. Sometimes users are given cash incentives and other inducements
to motivate them to change.
CRM, ERP, and EAI are three enterprise information systems that we will define and discuss
in Q7-4.