Page 332 -
P. 332
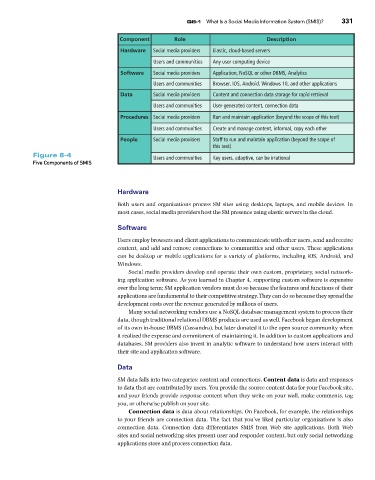
%QORQPGPV 4QNG Q8-1 What Is a Social Media Information System (SMIS)? 331
&GUETKRVKQP
*CTFYCTG Social media providers Elastic, cloud-based servers
Users and communities Any user computing device
5QHVYCTG Social media providers Application, NoSQL or other DBMS, Analytics
Users and communities Browser, IOS, Android, Windows 10, and other applications
&CVC Social media providers Content and connection data storage for rapid retrieval
Users and communities User-generated content, connection data
2TQEGFWTGU Social media providers Run and maintain application (beyond the scope of this text)
Users and communities Create and manage content, informal, copy each other
2GQRNG Social media providers Staff to run and maintain application (beyond the scope of
this text)
Figure 8-4 Users and communities Key users, adaptive, can be irrational
Five Components of SMIS
Hardware
Both users and organizations process SM sites using desktops, laptops, and mobile devices. In
most cases, social media providers host the SM presence using elastic servers in the cloud.
Software
Users employ browsers and client applications to communicate with other users, send and receive
content, and add and remove connections to communities and other users. These applications
can be desktop or mobile applications for a variety of platforms, including iOS, Android, and
Windows.
Social media providers develop and operate their own custom, proprietary, social network-
ing application software. As you learned in Chapter 4, supporting custom software is expensive
over the long term; SM application vendors must do so because the features and functions of their
applications are fundamental to their competitive strategy. They can do so because they spread the
development costs over the revenue generated by millions of users.
Many social networking vendors use a NoSQL database management system to process their
data, though traditional relational DBMS products are used as well. Facebook began development
of its own in-house DBMS (Cassandra), but later donated it to the open source community when
it realized the expense and commitment of maintaining it. In addition to custom applications and
databases, SM providers also invest in analytic software to understand how users interact with
their site and application software.
Data
SM data falls into two categories: content and connections. Content data is data and responses
to data that are contributed by users. You provide the source content data for your Facebook site,
and your friends provide response content when they write on your wall, make comments, tag
you, or otherwise publish on your site.
Connection data is data about relationships. On Facebook, for example, the relationships
to your friends are connection data. The fact that you’ve liked particular organizations is also
connection data. Connection data differentiates SMIS from Web site applications. Both Web
sites and social networking sites present user and responder content, but only social networking
applications store and process connection data.