Page 129 - Video Coding for Mobile Communications Efficiency, Complexity, and Resilience
P. 129
106 Chapter 4. Basic Motion Estimation Techniques
reference frame
search window current frame
M d mx
d ,d )
( x
y
+
N N 2 d my
best match
block current block
d my
+
M 2 d mx
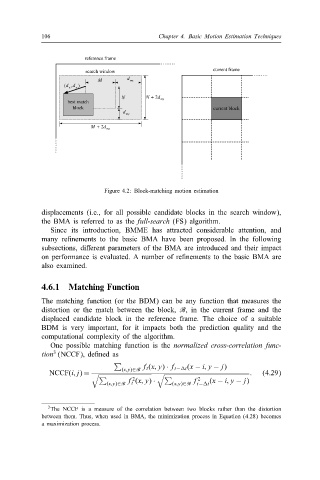
Figure 4.2: Block-matching motion estimation
displacements (i.e., for all possible candidate blocks in the search window),
the BMA is referred to as the full-search (FS) algorithm.
Since its introduction, BMME has attracted considerable attention, and
many re nements to the basic BMA have been proposed. In the following
subsections, di erent parameters of the BMA are introduced and their impact
on performance is evaluated. A number of re nements to the basic BMA are
also examined.
4.6.1 Matching Function
The matching function (or the BDM) can be any function that measures the
distortion or the match between the block, B, in the current frame and the
displaced candidate block in the reference frame. The choice of a suitable
BDM is very important, for it impacts both the prediction quality and the
computational complexity of the algorithm.
One possible matching function is the normalized cross-correlation func-
3
tion (NCCF), de ned as
(x;y)∈B f t (x; y) · f t−@t (x − i; y − j)
: (4.29)
NCCF(i; j)= 2 2
t
(x;y)∈B f (x; y) · (x;y)∈B f t−@t (x − i; y − j)
3 The NCCF is a measure of the correlation between two blocks rather than the distortion
between them. Thus, when used in BMA, the minimization process in Equation (4.28) becomes
a maximization process.