Page 220 - Video Coding for Mobile Communications Efficiency, Complexity, and Resilience
P. 220
Section 8.6. Simplex Minimization for Multiple-Reference Motion Estimation 197
QSIF Foreman @ 8.33 f.p.s. QSIF Foreman @ 8.33 f.p.s.
30.5 10 7
M=50 M=50
30
M=10 10 6
29.5 M=10
PSNR Y (dB) 29 M=5 Searched locations/frame M=5
28.5 10 5 M=2
M=2 M=1
28
M=1
27.5 10 4
0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50
Memory size (frames) Memory size (frames)
(a) Prediction quality (b) Computational complexity
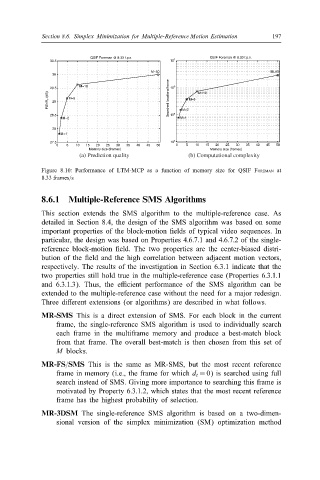
Figure 8.10: Performance of LTM-MCP as a function of memory size for QSIF FOREMAN at
8:33 frames=s
8.6.1 Multiple-Reference SMS Algorithms
This section extends the SMS algorithm to the multiple-reference case. As
detailed in Section 8.4, the design of the SMS algorithm was based on some
important properties of the block-motion :elds of typical video sequences. In
particular, the design was based on Properties 4:6:7:1 and 4:6:7:2 of the single-
reference block-motion :eld. The two properties are the center-biased distri-
bution of the :eld and the high correlation between adjacent motion vectors,
respectively. The results of the investigation in Section 6.3.1 indicate that the
two properties still hold true in the multiple-reference case (Properties 6:3:1:1
and 6:3:1:3). Thus, the eDcient performance of the SMS algorithm can be
extended to the multiple-reference case without the need for a major redesign.
Three di+erent extensions (or algorithms) are described in what follows.
MR-SMS This is a direct extension of SMS. For each block in the current
frame, the single-reference SMS algorithm is used to individually search
each frame in the multiframe memory and produce a best-match block
from that frame. The overall best-match is then chosen from this set of
M blocks.
MR-FS=SMS This is the same as MR-SMS, but the most recent reference
frame in memory (i.e., the frame for which d t = 0) is searched using full
search instead of SMS. Giving more importance to searching this frame is
motivated by Property 6:3:1:2, which states that the most recent reference
frame has the highest probability of selection.
MR-3DSM The single-reference SMS algorithm is based on a two-dimen-
sional version of the simplex minimization (SM) optimization method