Page 229 - Video Coding for Mobile Communications Efficiency, Complexity, and Resilience
P. 229
206 Chapter 9. Error-Resilience Video Coding Techniques
ENCODER
Video
in Waveform Entropy
encoder encoder Channel encoder
Source encoder
Channel
Video
out Waveform Entropy
decoder decoder Channel decoder
Source decoder
DECODER
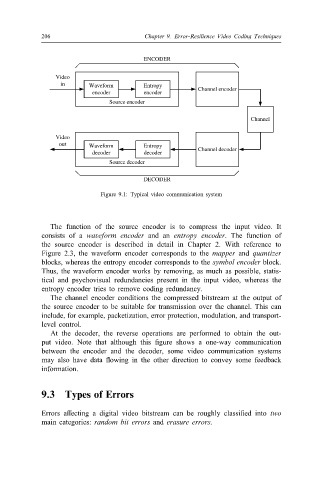
Figure 9.1: Typical video communication system
The function of the source encoder is to compress the input video. It
consists of a waveform encoder and an entropy encoder. The function of
the source encoder is described in detail in Chapter 2. With reference to
Figure 2.3, the waveform encoder corresponds to the mapper and quantizer
blocks, whereas the entropy encoder corresponds to the symbol encoder block.
Thus, the waveform encoder works by removing, as much as possible, statis-
tical and psychovisual redundancies present in the input video, whereas the
entropy encoder tries to remove coding redundancy.
The channel encoder conditions the compressed bitstream at the output of
the source encoder to be suitable for transmission over the channel. This can
include, for example, packetization, error protection, modulation, and transport-
level control.
At the decoder, the reverse operations are performed to obtain the out-
put video. Note that although this gure shows a one-way communication
between the encoder and the decoder, some video communication systems
may also have data 5owing in the other direction to convey some feedback
information.
9.3 Types of Errors
Errors a ecting a digital video bitstream can be roughly classi ed into two
main categories: random bit errors and erasure errors.