Page 58 - Video Coding for Mobile Communications Efficiency, Complexity, and Resilience
P. 58
Section 2.6. Intraframe Coding 35
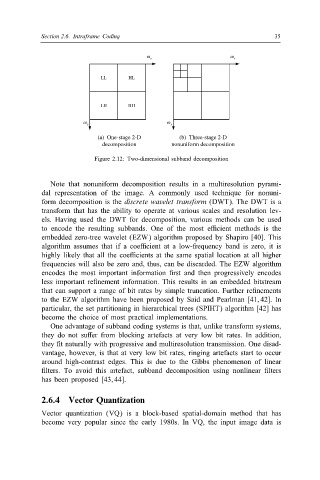
ω ω x
x
LL HL
LH HH
ω y ω y
(a) One-stage 2-D (b) Three-stage 2-D
decomposition nonuniform decomposition
Figure 2.12: Two-dimensional subband decomposition
Note that nonuniform decomposition results in a multiresolution pyrami-
dal representation of the image. A commonly used technique for nonuni-
form decomposition is the discrete wavelet transform (DWT). The DWT is a
transform that has the ability to operate at various scales and resolution lev-
els. Having used the DWT for decomposition, various methods can be used
to encode the resulting subbands. One of the most eGcient methods is the
embedded zero-tree wavelet (EZW) algorithm proposed by Shapiro [40]. This
algorithm assumes that if a coeGcient at a low-frequency band is zero, it is
highly likely that all the coeGcients at the same spatial location at all higher
frequencies will also be zero and, thus, can be discarded. The EZW algorithm
encodes the most important information rst and then progressively encodes
less important re nement information. This results in an embedded bitstream
that can support a range of bit rates by simple truncation. Further re nements
to the EZW algorithm have been proposed by Said and Pearlman [41, 42]. In
particular, the set partitioning in hierarchical trees (SPIHT) algorithm [42] has
become the choice of most practical implementations.
One advantage of subband coding systems is that, unlike transform systems,
they do not su6er from blocking artefacts at very low bit rates. In addition,
they t naturally with progressive and multiresolution transmission. One disad-
vantage, however, is that at very low bit rates, ringing artefacts start to occur
around high-contrast edges. This is due to the Gibbs phenomenon of linear
lters. To avoid this artefact, subband decomposition using nonlinear lters
has been proposed [43, 44].
2.6.4 Vector Quantization
Vector quantization (VQ) is a block-based spatial-domain method that has
become very popular since the early 1980s. In VQ, the input image data is