Page 263 - Vogel's TEXTBOOK OF QUANTITATIVE CHEMICAL ANALYSIS
P. 263
CHAPTER 9
CAS CHROMATOGRAPHY
9.1 INTRODUCTION
Gas chromatography is a process by which a mixture is separated into its
constituents by a moving gas phase passing over a stationary sorbent. The
technique is thus similar to liquid-liquid chromatography except that the mobile
liquid phase is replaced by a moving gas phase. Gas chromatography is divided
into two major categories: gas-liquid chromatography (GLC), where separation
occurs by partitioning a sample between a mobile gas phase and a thin layer
of non-volatile liquid coated on an inert support, and gas-solid chromatography
(GSC), which employs a solid of large surface area as the stationary phase. The
present chapter deals with gas-liquid chromatography and some of its
applications in the field of quantitative chemical analysis. However, before
considering these applications it is appropriate to describe briefly the apparatus
used in, and some of the basic principles of, gas chromatography. A comprehensive
account of the various aspects of modern gas chromatography is, of course,
beyond the scope of the present text and, for more detailed accounts of these
topics the texts listed in the Bibliography at the end of this chapter should be
consulted.
9.2 APPARATUS
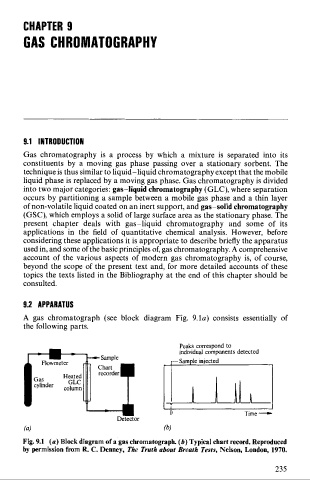
A gas chromatograph (see block diagram Fig. 9.1~) consists essentially of
the following parts.
Peaks correspond to
individual companents detected
r Sample injected
r I
Time -
O
Detector
Fig. 9.1 (a) Block diagram of a gas chromatograph. (b) Typical chart record. Reproduced
by permission from R. C. Denney, The Truth about Breath Tests, Nelson, London, 1970.