Page 265 - Materials Chemistry, Second Edition
P. 265
CAT3525_C08.qxd 1/29/2005 10:03 AM Page 236
236 Waste Management Practices: Municipal, Hazardous, and Industrial
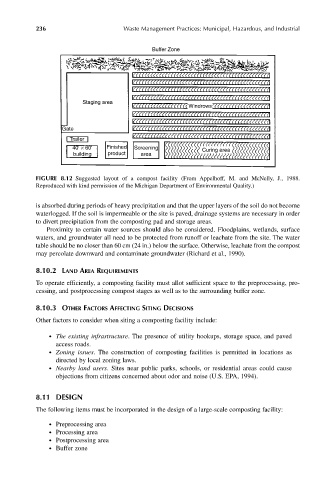
Buffer Zone
Staging area
Windrows
Gate
Trailer
40' × 60' Finished Screening Curing area
building product area
FIGURE 8.12 Suggested layout of a compost facility (From Appelhoff, M. and McNelly, J., 1988.
Reproduced with kind permission of the Michigan Department of Environmental Quality.)
is absorbed during periods of heavy precipitation and that the upper layers of the soil do not become
waterlogged. If the soil is impermeable or the site is paved, drainage systems are necessary in order
to divert precipitation from the composting pad and storage areas.
Proximity to certain water sources should also be considered. Floodplains, wetlands, surface
waters, and groundwater all need to be protected from runoff or leachate from the site. The water
table should be no closer than 60 cm (24 in.) below the surface. Otherwise, leachate from the compost
may percolate downward and contaminate groundwater (Richard et al., 1990).
8.10.2 LAND AREA REQUIREMENTS
To operate efficiently, a composting facility must allot sufficient space to the preprocessing, pro-
cessing, and postprocessing compost stages as well as to the surrounding buffer zone.
8.10.3 OTHER FACTORS AFFECTING SITING DECISIONS
Other factors to consider when siting a composting facility include:
● The existing infrastructure. The presence of utility hookups, storage space, and paved
access roads.
● Zoning issues. The construction of composting facilities is permitted in locations as
directed by local zoning laws.
● Nearby land users. Sites near public parks, schools, or residential areas could cause
objections from citizens concerned about odor and noise (U.S. EPA, 1994).
8.11 DESIGN
The following items must be incorporated in the design of a large-scale composting facility:
● Preprocessing area
● Processing area
● Postprocessing area
● Buffer zone