Page 339 - Materials Chemistry, Second Edition
P. 339
CAT3525_C10.qxd 1/31/2005 12:00 PM Page 310
310 Waste Management Practices: Municipal, Hazardous, and Industrial
10.4.14.5 Generation of Landfill Gases
Gases occurring in active and closed landfills include methane (CH ), carbon dioxide (CO ), carbon
2
4
monoxide (CO), hydrogen (H ), hydrogen sulfide (H S), ammonia (NH ), nitrogen (N ), and oxygen
2
2
2
3
(O ). The most common gases produced within landfills are CH and CO , with lesser amounts of the
2
4
2
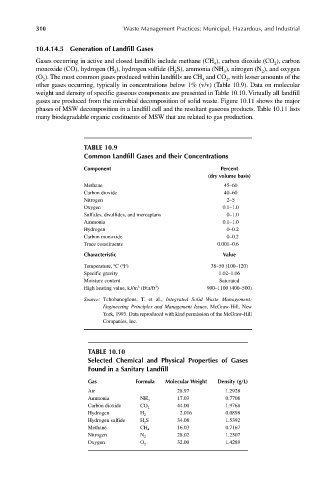
other gases occurring, typically in concentrations below 1% (v/v) (Table 10.9). Data on molecular
weight and density of specific gaseous components are presented in Table 10.10. Virtually all landfill
gases are produced from the microbial decomposition of solid waste. Figure 10.11 shows the major
phases of MSW decomposition in a landfill cell and the resultant gaseous products. Table 10.11 lists
many biodegradable organic costituents of MSW that are related to gas production.
TABLE 10.9
Common Landfill Gases and their Concentrations
Component Percent
(dry volume basis)
Methane 45–60
Carbon dioxide 40–60
Nitrogen 2–5
Oxygen 0.1–1.0
Sulfides, disulfides, and mercaptans 0–1.0
Ammonia 0.1–1.0
Hydrogen 0–0.2
Carbon monoxide 0–0.2
Trace constituents 0.001–0.6
Characteristic Value
o
o
Temperature, C ( F) 38–50 (100–120)
Specific gravity 1.02–1.06
Moisture content Saturated
3
3
High heating value, kJ/m (Btu/ft ) 900–1100 (400–500)
Source: Tchobanoglous, T. et al., Integrated Solid Waste Management:
Engineering Principles and Management Issues, McGraw-Hill, New
York, 1993. Data reproduced with kind permission of the McGraw-Hill
Companies, Inc.
TABLE 10.10
Selected Chemical and Physical Properties of Gases
Found in a Sanitary Landfill
Gas Formula Molecular Weight Density (g/L)
Air 28.97 1.2928
Ammonia NH 3 17.03 0.7708
Carbon dioxide CO 2 44.00 1.9768
Hydrogen H 2 2.016 0.0898
Hydrogen sulfide H S 34.08 1.5392
2
Methane CH 4 16.03 0.7167
Nitrogen N 2 28.02 1.2507
Oxygen O 2 32.00 1.4289