Page 344 - Materials Chemistry, Second Edition
P. 344
CAT3525_C10.qxd 1/31/2005 12:00 PM Page 315
The Sanitary Landfill 315
amount of gas that can be derived from the rapidly and slowly decomposable organic constituents
in MSW. Note that some of the yard wastes will decompose rapidly (e.g., grass clippings) while oth-
ers will be more stable (branches).
SOLUTION
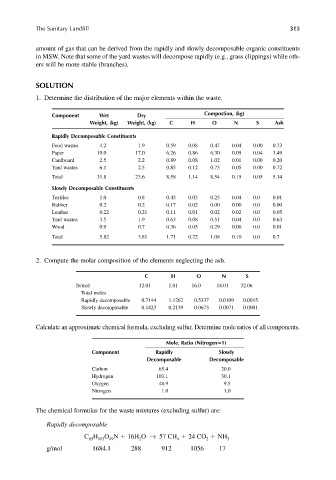
1. Determine the distribution of the major elements within the waste.
Component Wet Dry Compostion, (kg)
Weight, (kg) Weight, (kg) C H O N S Ash
Rapidly Decomposable Constituents
Food wastes 4.2 1.9 0.59 0.08 0.47 0.04 0.00 0.73
Paper 19.0 17.0 6.26 0.86 6.30 0.05 0.04 3.49
Cardboard 2.5 2.2 0.89 0.08 1.02 0.01 0.00 0.20
Yard wastes 6.1 2.5 0.85 0.12 0.75 0.05 0.00 0.72
Total 31.8 23.6 8.58 1.14 8.54 0.15 0.05 5.14
Slowly Decomposable Constituents
Textiles 1.0 0.8 0.45 0.05 0.25 0.04 0.0 0.01
Rubber 0.2 0.2 0.17 0.02 0.00 0.00 0.0 0.00
Leather 0.22 0.21 0.11 0.01 0.02 0.02 0.0 0.05
Yard wastes 3.5 1.9 0.63 0.08 0.51 0.04 0.0 0.63
Wood 0.9 0.7 0.36 0.05 0.29 0.00 0.0 0.01
Total 5.82 3.81 1.71 0.22 1.08 0.10 0.0 0.7
2. Compute the molar composition of the elements neglecting the ash.
C H O N S
lb/mol 12.01 1.01 16.0 14.01 32.06
Total moles
Rapidly decomposable 0.7144 1.1262 0.5337 0.0109 0.0015
Slowly decomposable 0.1423 0.2139 0.0673 0.0071 0.0001
Calculate an approximate chemical formula, excluding sulfur. Determine mole ratios of all components.
Mole. Ratio (Nitrogen 1)
Component Rapidly Slowly
Decomposable Decomposable
Carbon 65.4 20.0
Hydrogen 103.1 30.1
Oxygen 48.9 9.5
Nitrogen 1.0 1.0
The chemical formulas for the waste mixtures (excluding sulfur) are:
Rapidly decomposable
C H O N 16H O → 57 CH 24 CO NH 3
4
2
103
65
2
49
g/mol 1684.1 288 912 1056 17