Page 432 - Materials Chemistry, Second Edition
P. 432
CAT3525_C12.qxd 1/27/2005 4:11 PM Page 403
Hazardous Waste Generator Requirements 403
For tank systems, the generator must:
● Label each tank with the words “Hazardous Waste.”
● Mark each with the beginning of the accumulation period.
● For those tanks equipped with an automatic waste feed, a feed cutoff or bypass system
must be installed in the event of an overflow.
● Inspect monitoring equipment and the level of waste in uncovered tanks at least once per
day. Inspect the tanks and surrounding areas for leaks and corrosion at least weekly.
● Use the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) buffer zone requirements for cov-
ered tanks containing ignitable or reactive wastes.
● Not mix incompatible wastes.
● Provide at least 2 ft of freeboard (i.e., space at the top of each tank) in uncovered tanks,
unless the tank is equipped with a containment structure.
● Report spills from a tank system to the state regulatory agency.
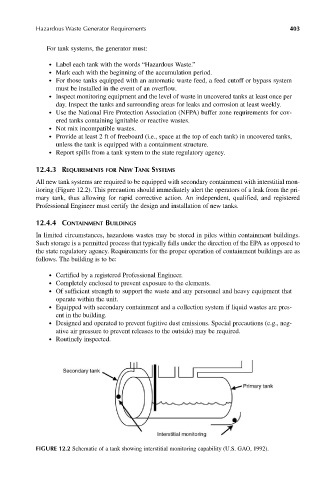
12.4.3 REQUIREMENTS FOR NEW TANK SYSTEMS
All new tank systems are required to be equipped with secondary containment with interstitial mon-
itoring (Figure 12.2). This precaution should immediately alert the operators of a leak from the pri-
mary tank, thus allowing for rapid corrective action. An independent, qualified, and registered
Professional Engineer must certify the design and installation of new tanks.
12.4.4 CONTAINMENT BUILDINGS
In limited circumstances, hazardous wastes may be stored in piles within containment buildings.
Such storage is a permitted process that typically falls under the direction of the EPA as opposed to
the state regulatory agency. Requirements for the proper operation of containment buildings are as
follows. The building is to be:
● Certified by a registered Professional Engineer.
● Completely enclosed to prevent exposure to the elements.
● Of sufficient strength to support the waste and any personnel and heavy equipment that
operate within the unit.
● Equipped with secondary containment and a collection system if liquid wastes are pres-
ent in the building.
● Designed and operated to prevent fugitive dust emissions. Special precautions (e.g., neg-
ative air pressure to prevent releases to the outside) may be required.
● Routinely inspected.
FIGURE 12.2 Schematic of a tank showing interstitial monitoring capability (U.S. GAO, 1992).